Page 343 - Read Online
P. 343
Page 6 of 13 Kumar et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:35 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.006
Figure 4. Stress-stretch curve for intima vessel [13]
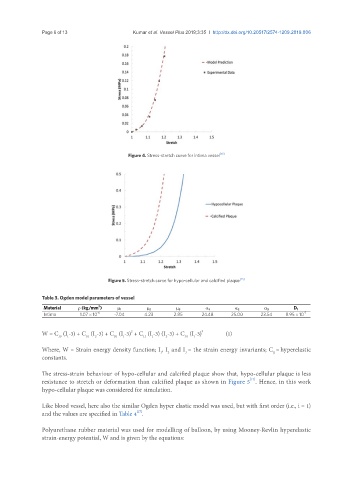
Figure 5. Stress-stretch curve for hypo-cellular and calcified plaque [13]
Table 3. Ogden model parameters of vessel
3
Material ρ (kg/mm ) µ 1 µ 2 µ 3 α 1 α 2 α 3 D 1
Intima 1.07 × 10 -6 -7.04 4.23 2.85 24.48 25.00 23.54 8.95 × 10 -7
2
3
W = C (I -3) + C (I -3) + C (I -3) + C (I -3) (I -3) + C (I -3) (1)
20
1
30
1
2
11
1
2
10
1
01
Where, W = Strain energy density function; I , I and I = the strain energy invariants; C = hyperelastic
3
1
2
ij
constants.
The stress-strain behaviour of hypo-cellular and calcified plaque show that, hypo-cellular plaque is less
[17]
resistance to stretch or deformation than calcified plaque as shown in Figure 5 . Hence, in this work
hypo-cellular plaque was considered for simulation.
Like blood vessel, here also the similar Ogden hyper elastic model was used, but with first order (i.e., i = 1)
[17]
and the values are specified in Table 4 .
Polyurethane rubber material was used for modelling of balloon, by using Mooney-Revlin hyperelastic
strain-energy potential, W and is given by the equations: