Page 184 - Read Online
P. 184
Sobenin et al. Is insulin atherogenic?
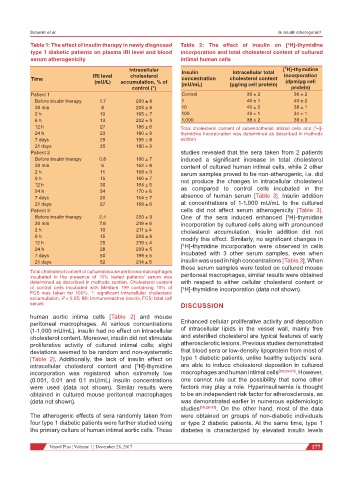
Table 1: The effect of insulin therapy in newly diagnosed Table 2: The effect of insulin on [ H]-thymidine
3
type 1 diabetic patients on plasma IRI level and blood incorporation and total cholesterol content of cultured
serum atherogenicity intimal human cells
3
Intracellular Insulin Intracellular total [ H]-thymidine
IRI level cholesterol incorporation
Time concentration cholesterol content
(mU/L) accumulation, % of (mU/mL) (µg/mg cell protein) (dpm/µg cell
control (*) protein)
Patient 1 Control 39 ± 2 36 ± 2
Before insulin therapy 1.7 200 ± 8 1 40 ± 1 40 ± 2
30 min 8 205 ± 6 10 40 ± 2 38 ± 1
2 h 10 195 ± 7 100 40 ± 1 34 ± 1
6 h 13 202 ± 5 1,000 38 ± 2 39 ± 3
12 h 27 186 ± 6 Total cholesterol content of subendothelial intimal cells and [ H]-
3
24 h 23 180 ± 9 thymidine incorporation was determined as described in methods
7 days 29 195 ± 8 section
21 days 35 180 ± 9
Patient 2 studies revealed that the sera taken from 2 patients
Before insulin therapy 0.8 160 ± 7 induced a significant increase in total cholesterol
30 min 6 162 ± 8 content of cultured human intimal cells, while 2 other
2 h 11 168 ± 3 serum samples proved to be non-atherogenic, i.e. did
6 h 15 160 ± 7 not produce the changes in intracellular cholesterol
12 h 30 164 ± 5
24 h 34 170 ± 6 as compared to control cells incubated in the
7 days 20 164 ± 7 absence of human serum [Table 3]. Insulin addition
21 days 27 169 ± 6 at concentrations of 1-1,000 mU/mL to the cultured
Patient 3 cells did not affect serum atherogenicity [Table 3].
3
Before insulin therapy 2.4 220 ± 9 One of the sera induced enhanced [ H]-thymidine
30 min 7.8 219 ± 6 incorporation by cultured cells along with pronounced
2 h 10 211 ± 4 cholesterol accumulation. Insulin addition did not
6 h 15 208 ± 6 modify this effect. Similarly, no significant changes in
12 h 25 219 ± 4 [ H]-thymidine incorporation were observed in cells
3
24 h 28 209 ± 5
7 days 50 199 ± 5 incubated with 3 other serum samples, even when
21 days 52 214 ± 5 insulin was used in high concentrations [Table 3]. When
these serum samples were tested on cultured mouse
Total cholesterol content of cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages
incubated in the presence of 10% tested patients’ serum was peritoneal macrophages, similar results were obtained
determined as described in methods section. Cholesterol content with respect to either cellular cholesterol content or
of control cells incubated with Medium 199 containing 10% of [ H]-thymidine incorporation (data not shown).
3
FCS was taken for 100%. *: significant intracellular cholesterol
accumulation, P < 0.05; IRI: immunoreactive insulin; FCS: fetal calf
serum DISCUSSION
human aortic intima cells [Table 2] and mouse
peritoneal macrophages. At various concentrations Enhanced cellular proliferative activity and deposition
(1-1,000 mU/mL), insulin had no effect on intracellular of intracellular lipids in the vessel wall, mainly free
cholesterol content. Moreover, insulin did not stimulate and esterified cholesterol are typical features of early
proliferative activity of cultured intimal cells; slight atherosclerotic lesions. Previous studies demonstrated
deviations seemed to be random and non-systematic that blood sera or low-density lipoprotein from most of
[Table 2]. Additionally, the lack of insulin effect on type 1 diabetic patients, unlike healthy subjects’ sera,
intracellular cholesterol content and [ H]-thymidine are able to induce cholesterol deposition in cultured
3
incorporation was registered when extremely low macrophages and human intimal cells [20,23-27] . However,
(0.001, 0.01 and 0.1 mU/mL) insulin concentrations one cannot rule out the possibility that some other
were used (data not shown). Similar results were factors may play a role. Hyperinsulinemia is thought
obtained in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages to be an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis, as
(data not shown). was demonstrated earlier in numerous epidemiologic
studies [10,28-31] . On the other hand, most of the data
The atherogenic effects of sera randomly taken from were obtained on groups of non-diabetic individuals
four type 1 diabetic patients were further studied using or type 2 diabetic patients. At the same time, type 1
the primary culture of human intimal aortic cells. These diabetes is characterized by elevated insulin levels
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 177