Page 17 - Read Online
P. 17
Page 6 of 24 Rao. Vessel Plus 2022;6:22 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.105
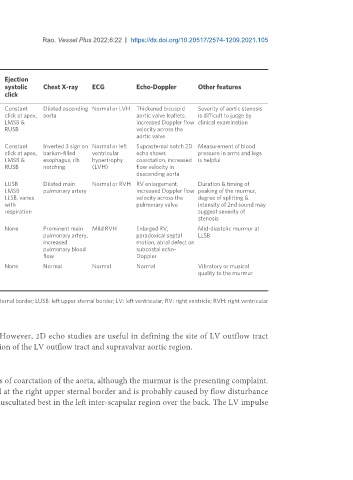
Table 4. Differential diagnosis of ejection systolic murmurs
Point of Radiation Ejection
maximal of the Precordial Thrill Femoral 2nd heart systolic Chest X-ray ECG Echo-Doppler Other features
intensity of murmur impulses pulses sound click
the murmur
Aortic RUSB Carotid Normal or RUSB & Normal Normal Constant Dilated ascending Normal or LVH Thickened bicuspid Severity of aortic stenosis
stenosis LMSB arteries increased LV suprasternal click at apex, aorta aortic valve leaflets, is difficult to judge by
impulse notch LMSB & increased Doppler flow clinical examination
RUSB velocity across the
aortic valve
Coarctation RUSB Carotid Normal or Suprasternal Decreased & Normal Constant Inverted 3 sign on Normal or left Suprasternal notch 2D Measurement of blood
of the aorta arteries increased LV notch delayed or click at apex, barium-filled ventricular echo shows pressure in arms and legs
impulse absent LMSB & esophagus, rib hypertrophy coarctation, increased is helpful
RUSB notching (LVH) flow velocity in
descending aorta
Pulmonary LUSB Infra- Normal or LSUB & Normal Normal, LUSB Dilated main Normal or RVH RV enlargement, Duration & timing of
stenosis clavicular increased RV suprasternal diminished, LMSB pulmonary artery increased Doppler flow peaking of the murmur,
regions & impulse notch or absent LLSB, varies velocity across the degree of splitting &
back with pulmonary valve intensity of 2nd sound may
respiration suggest severity of
stenosis
Atrial septal LUSB None Hyper- None Normal Widely split None Prominent main Mild RVH Enlarged RV, Mid-diastolic murmur at
defect dynamic RV and fixed pulmonary artery, paradoxical septal LLSB
impulse increased motion, atrial defect on
pulmonary blood subcostal echo-
flow Doppler
Functional or Between apex None Normal None Normal Normal None Normal Normal Normal Vibratory or musical
innocent & LLSB or at quality to the murmur
murmur LUSB
ECG: Electrocardiogram; RUSB: right upper sternal border; LMSB: left mid-sternal border; LLSB: left lower sternal border; LUSB: left upper sternal border; LV: left ventricular; RV: right ventricle; RVH: right ventricular
hypertrophy.
are present, and the murmur may be appreciated better at LLSB or LMSBs. However, 2D echo studies are useful in defining the site of LV outflow tract
obstruction. The severity of obstruction can be estimated by Doppler interrogation of the LV outflow tract and supravalvar aortic region.
Coarctation of the aorta
Simultaneous palpation of femoral and brachial pulses will lead to the diagnosis of coarctation of the aorta, although the murmur is the presenting complaint.
The ejection systolic murmur related to aortic coarctation may be auscultated at the right upper sternal border and is probably caused by flow disturbance
across the aortic valve. The murmur of flow across aortic coarctation may be auscultated best in the left inter-scapular region over the back. The LV impulse