Page 93 - Read Online
P. 93
Calafiore et al. Vessel Plus 2023;7:18 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2023.42 Page 7 of 21
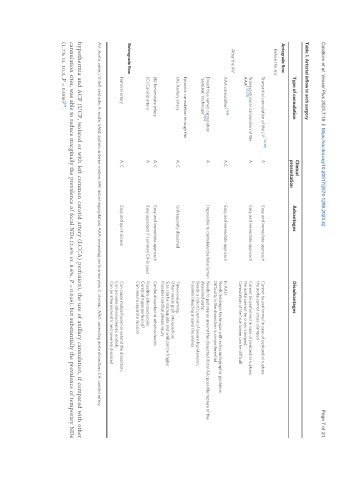
Table 1. Arterial inflow in arch surgery
Clinical
Type of cannulation Advantages Disadvantages
presentation
Antegrade flow
Before the AV
Transatrial cannulation of the LV [130,131] A Easy and immediate approach Cannot be performed in case of pericardial rupture
the aorta cannot cross-clamped
Transventricular cannulation of the A Easy and immediate approach Cannot be performed in case of pericardial rupture;
[132,133]
AAA the aorta cannot be cross-clamped;
Cannulation of the true lumen can be difficult
After the AV
[134]
AAA cannulation A,C Easy and immediate approach In AAD:
Needs Seldinger technique with echocardiographic guidance;
Difficulty is the dissection is circumferential
Direct true lumen cannulation A Impossible to cannulate the false lumen Needs to put snares around the dissected distal AA; possible rupture of the
[135]
“samurai” technique dissected aorta;
Needs a (short) period of severe hypotension;
Possible bleeding around the snares
Epiaortic cannulation through the
(A) Axillary artery A, C Unfrequently dissected Time-consuming;
Often needs graft interposition;
Size can be inadequate and wall can be fragile;
Possible brachial plexus injury
(B) Innominate artery A, C Easy and immediate approach Can be dissected or atherosclerotic
(C) Carotid artery A Easy approach if common CA is used Possible atherosclerosis;
Cerebral hyperperfusion?
Can need a separate incision
Retrograde flow
Femoral artery A, C Easy and quick access Can cause malperfusion or extend the dissection;
Can provoke atherosclerotic emboli;
Can be atherosclerotic and severely diseased
AV: Aortic valve; LV: left ventricle; A: acute; SAM: systolic anterior motion; MR: mitral regurgitation; AAA: ascending aorta aneurysm; C: chronic; AAD: ascending aorta dissection; CA: carotid artery.
hypothermia and ACP (UCP, isolated or with left common carotid artery (LCCA) perfusion), the use of axillary cannulation, if compared with other
cannulation sites, was able to reduce marginally the prevalence of focal NDs (2.6% vs. 8.6%, P = 0.046), but substantially the prevalence of temporary NDs
[35]
(1.7% vs. 10.3, P = 0.006) .