Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
He et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:37 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.32 Page 21 of 27
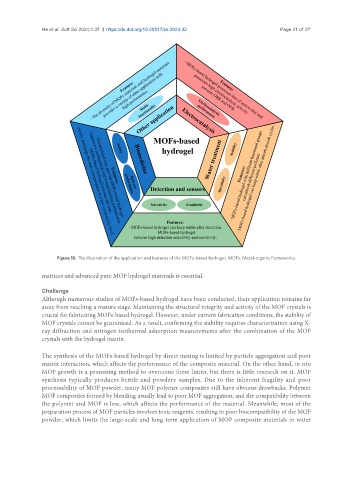
Figure 10. The illustration of the application and features of the MOFs-based hydrogel. MOFs: Metal-organic frameworks.
matrices and advanced pure MOF hydrogel materials is essential.
Challenge
Although numerous studies of MOFs-based hydrogel have been conducted, their application remains far
away from reaching a mature stage. Maintaining the structural integrity and activity of the MOF crystals is
crucial for fabricating MOFs-based hydrogel. However, under current fabrication conditions, the stability of
MOF crystals cannot be guaranteed. As a result, confirming the stability requires characterization using X-
ray diffraction and nitrogen isothermal adsorption measurements after the combination of the MOF
crystals with the hydrogel matrix.
The synthesis of the MOFs-based hydrogel by direct mixing is limited by particle aggregation and poor
matrix interaction, which affects the performance of the composite material. On the other hand, in situ
MOF growth is a promising method to overcome these limits, but there is little research on it. MOF
synthesis typically produces brittle and powdery samples. Due to the inherent fragility and poor
processability of MOF powder, many MOF polymer composites still have obvious drawbacks. Polymer
MOF composites formed by blending usually lead to poor MOF aggregation, and the compatibility between
the polymer and MOF is low, which affects the performance of the material. Meanwhile, most of the
preparation process of MOF particles involves toxic reagents, resulting in poor biocompatibility of the MOF
powder, which limits the large-scale and long-term application of MOF composite materials in water