Page 14 - Read Online
P. 14
Page 12 of 27 He et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:37 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.32
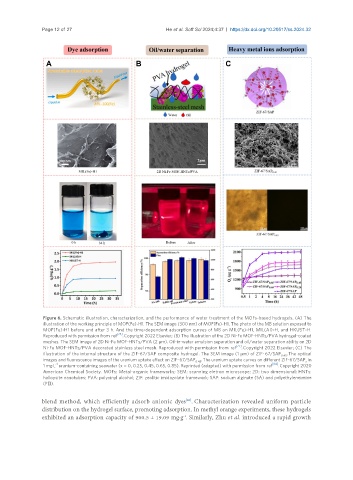
Figure 6. Schematic illustration, characterization, and the performance of water treatment of the MOFs-based hydrogels. (A) The
illustration of the working principle of MOF(Fe)-H1. The SEM image (300 nm) of MOF(Fe)-H1. The photo of the MB solution exposed to
MOF(Fe)-H1 before and after 3 h. And the time-dependent adsorption curves of MB on MIL(Fe)-H1, MIL(Al)-H, and HKUST-H.
Reproduced with permission from ref [76] . Copyright 2022 Elsevier; (B) The illustration of the 2D Ni-Fe MOF-HNTs/PVA hydrogel-coated
meshes. The SEM image of 2D Ni-Fe MOF-HNTs/PVA (2 μm). Oil-in-water emulsion separation and oil/water separation ability on 2D
Ni-Fe MOF-HNTs/PVA decorated stainless steel mesh. Reproduced with permission from ref [77] . Copyright 2022 Elsevier; (C) The
illustration of the internal structure of the ZIF-67/SAP composite hydrogel. The SEM image (1 μm) of ZIF-67/SAP 0.45 . The optical
images and fluorescence images of the uranium uptake effect on ZIF-67/SAP 0.45 . The uranium uptake curves on different ZIF-67/SAP in
x
-1
1 mg·L uranium-containing seawater (x = 0, 0.25, 0.45, 0.65, 0.85). Reprinted (adapted) with permission from ref [84] . Copyright 2020
American Chemical Society. MOFs: Metal-organic frameworks; SEM: scanning eletron microscope; 2D: two dimensional; HNTs:
halloysite nanotubes; PVA: polyvinyl alcohol; ZIF: zeolitic imidazolate framework; SAP: sodium alginate (SA) and polyethyleneimine
(PEI).
[82]
blend method, which efficiently adsorb anionic dyes . Characterization revealed uniform particle
distribution on the hydrogel surface, promoting adsorption. In methyl orange experiments, these hydrogels
exhibited an adsorption capacity of 900.5 ± 19.09 mg·g . Similarly, Zhu et al. introduced a rapid growth
-1