Page 5 - Read Online
P. 5
Kim et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:12 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.50 Page 3 of 11
Table 1. Current state-of-art computer vision techniques used in soft electronics
Fiducial Frame of Processing Resolution E.g., in soft
*
Category Applications Key outputs Dimensionality Ref.
points reference time electronics
Particle image Fluid flow Velocity vorticity Yes Eulerian 2D Long High Respiratory [10]
velocimetry sensors
Particle Fluid flow Velocity Yes Lagrangian 2D, 3D Intermediate High (2D), Drug delivery [23]
tracking object tracking trajectory (Volumetric) (2D), long medium systems
velocimetry (3D) (3D)
Digital image Solid Deformation Yes Eulerian 2D, 3D Short (2D), High (2D), Haptic [25]
correlation deformation strain lagrangian (Stereoscopic) intermediate high (3D) systems strain
(3D) sensors
Eulerian video Visual Spatiotemporally No N/A 2D Short Qualitative Cardiac [18]
magnification enhancement amplified video sensors
Structure 3D geometry 3D volumetric No N/A 3D Intermediate Qualitative 3D buckled [19]
from motion estimation image (Volumetric) electronics
Area tracking Solid Deformation No Lagrangian 2D Intermediate Low to Organoid [20]
deformation medium sensors
Markerless Object Trajectory No Lagrangian 2D, 3D Intermediate Low (2D, Biomechanical [17]
pose tracking (Volumetric) (2D), long 3D) sensors
estimation (3D)
* 3 3 2 2
Typically, High > 10 , 10 > Medium > 10 , and 10 > Low in data points. 3D: Three-dimensional.
[8]
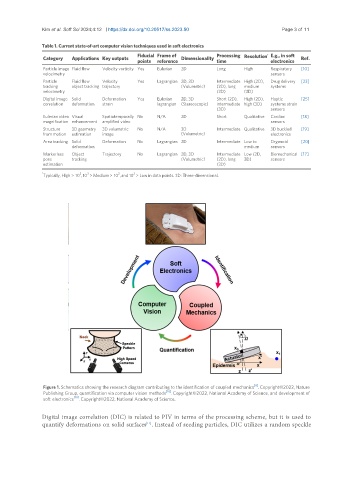
Figure 1. Schematics showing the research diagram contributing to the identification of coupled mechanics . Copyright©2022, Nature
[10]
Publishing Group, quantification via computer vision methods . Copyright©2022, National Academy of Science, and development of
[10]
soft electronics . Copyright©2022, National Academy of Science.
Digital image correlation (DIC) is related to PIV in terms of the processing scheme, but it is used to
[11]
quantify deformations on solid surfaces . Instead of seeding particles, DIC utilizes a random speckle