Page 112 - Read Online
P. 112
Page 6 of 21 Zhang et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:23 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.58
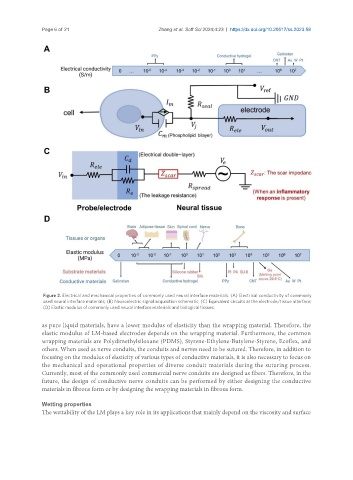
Figure 2. Electrical and mechanical properties of commonly used neural interface materials. (A) Electrical conductivity of commonly
used neural interface materials; (B) Neuroelectric signal acquisition schematic; (C) Equivalent circuits at the electrode/tissue interface;
(D) Elastic modulus of commonly used neural interface materials and biological tissues.
as pure liquid materials, have a lower modulus of elasticity than the wrapping material. Therefore, the
elastic modulus of LM-based electrodes depends on the wrapping material. Furthermore, the common
wrapping materials are Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), Styrene-Ethylene-Butylene-Styrene, Ecoflex, and
others. When used as nerve conduits, the conduits and nerves need to be sutured. Therefore, in addition to
focusing on the modulus of elasticity of various types of conductive materials, it is also necessary to focus on
the mechanical and operational properties of diverse conduit materials during the suturing process.
Currently, most of the commonly used commercial nerve conduits are designed as fibers. Therefore, in the
future, the design of conductive nerve conduits can be performed by either designing the conductive
materials in fibrous form or by designing the wrapping materials in fibrous form.
Wetting properties
The wettability of the LM plays a key role in its applications that mainly depend on the viscosity and surface