Page 69 - Read Online
P. 69
Nagwade et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:24 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.12 Page 3 of 25
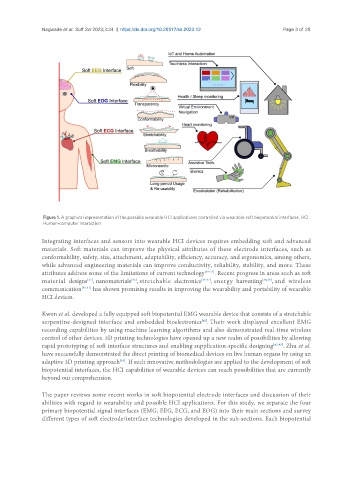
Figure 1. A graphical representation of the possible wearable HCI applications controlled via wearable soft biopotential interfaces. HCI:
Human-computer interaction.
Integrating interfaces and sensors into wearable HCI devices requires embedding soft and advanced
materials. Soft materials can improve the physical attributes of these electrode interfaces, such as
conformability, safety, size, attachment, adaptability, efficiency, accuracy, and ergonomics, among others,
while advanced engineering materials can improve conductivity, reliability, stability, and more. These
attributes address some of the limitations of current technology [29-31] . Recent progress in areas such as soft
[32]
[33]
material designs , nanomaterials , stretchable electronics [34-37] , energy harvesting [38,39] , and wireless
communication [40,41] has shown promising results in improving the wearability and portability of wearable
HCI devices.
Kwon et al. developed a fully equipped soft biopotential EMG wearable device that consists of a stretchable
serpentine-designed interface and embedded bioelectronics . Their work displayed excellent EMG
[42]
recording capabilities by using machine learning algorithms and also demonstrated real-time wireless
control of other devices. 3D printing technologies have opened up a new realm of possibilities by allowing
rapid prototyping of soft interface structures and enabling supplication-specific designing [43-45] . Zhu et al.
have successfully demonstrated the direct printing of biomedical devices on live human organs by using an
adaptive 3D printing approach . If such innovative methodologies are applied to the development of soft
[46]
biopotential interfaces, the HCI capabilities of wearable devices can reach possibilities that are currently
beyond our comprehension.
The paper reviews some recent works in soft biopotential electrode interfaces and discussion of their
abilities with regard to wearability and possible HCI applications. For this study, we separate the four
primary biopotential signal interfaces (EMG, EEG, ECG, and EOG) into their main sections and survey
different types of soft electrode/interface technologies developed in the sub-sections. Each biopotential