Page 38 - Read Online
P. 38
Page 10 of 38 Wei et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.09
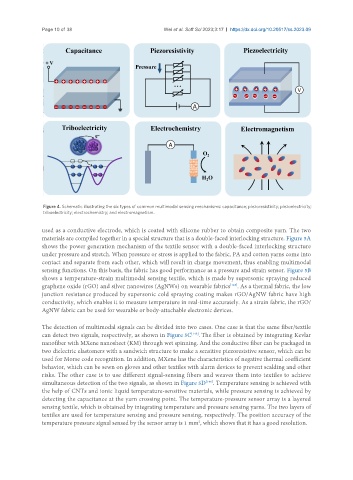
Figure 4. Schematic illustrating the six types of common multimodal sensing mechanisms: capacitance; piezoresistivity; piezoelectricity;
triboelectricity; electrochemistry; and electromagnetism.
used as a conductive electrode, which is coated with silicone rubber to obtain composite yarn. The two
materials are compiled together in a special structure that is a double-faced interlocking structure. Figure 5A
shows the power generation mechanism of the textile sensor with a double-faced interlocking structure
under pressure and stretch. When pressure or stress is applied to the fabric, PA and cotton yarns come into
contact and separate from each other, which will result in charge movement, thus enabling multimodal
sensing functions. On this basis, the fabric has good performance as a pressure and strain sensor. Figure 5B
shows a temperature-strain multimodal sensing textile, which is made by supersonic spraying reduced
graphene oxide (rGO) and silver nanowires (AgNWs) on wearable fabrics . As a thermal fabric, the low
[143]
junction resistance produced by supersonic cold spraying coating makes rGO/AgNW fabric have high
conductivity, which enables it to measure temperature in real-time accurately. As a strain fabric, the rGO/
AgNW fabric can be used for wearable or body-attachable electronic devices.
The detection of multimodal signals can be divided into two cases. One case is that the same fiber/textile
can detect two signals, respectively, as shown in Figure 5C . The fiber is obtained by integrating Kevlar
[145]
nanofiber with MXene nanosheet (KM) through wet spinning. And the conductive fiber can be packaged in
two dielectric elastomers with a sandwich structure to make a sensitive piezoresistive sensor, which can be
used for Morse code recognition. In addition, MXene has the characteristics of negative thermal coefficient
behavior, which can be sewn on gloves and other textiles with alarm devices to prevent scalding and other
risks. The other case is to use different signal-sensing fibers and weaves them into textiles to achieve
[146]
simultaneous detection of the two signals, as shown in Figure 5D . Temperature sensing is achieved with
the help of CNTs and ionic liquid temperature-sensitive materials, while pressure sensing is achieved by
detecting the capacitance at the yarn crossing point. The temperature-pressure sensor array is a layered
sensing textile, which is obtained by integrating temperature and pressure sensing yarns. The two layers of
textiles are used for temperature sensing and pressure sensing, respectively. The position accuracy of the
temperature pressure signal sensed by the sensor array is 1 mm , which shows that it has a good resolution.
2