Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
Wei et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.09 Page 11 of 38
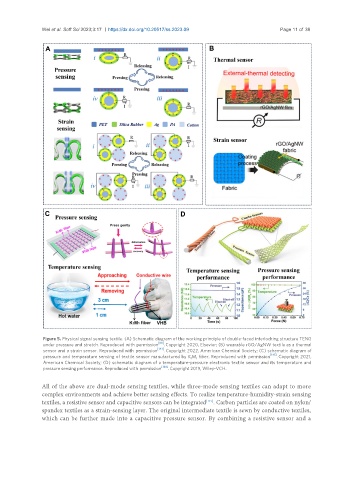
Figure 5. Physical signal sensing textile. (A) Schematic diagram of the working principle of double-faced interlocking structure TENG
under pressure and stretch. Reproduced with permission [68] . Copyright 2020, Elsevier; (B) wearable rGO/AgNW textile as a thermal
sensor and a strain sensor. Reproduced with permission [143] . Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society; (C) schematic diagram of
pressure and temperature sensing of textile sensor manufactured by K M fiber. Reproduced with permission [145] . Copyright 2021,
1
1
American Chemical Society; (D) schematic diagram of a temperature-pressure electronic textile sensor and its temperature and
pressure sensing performance. Reproduced with permission [146] . Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH.
All of the above are dual-mode sensing textiles, while three-mode sensing textiles can adapt to more
complex environments and achieve better sensing effects. To realize temperature-humidity-strain sensing
[147]
textiles, a resistive sensor and capacitive sensors can be integrated . Carbon particles are coated on nylon/
spandex textiles as a strain-sensing layer. The original intermediate textile is sewn by conductive textiles,
which can be further made into a capacitive pressure sensor. By combining a resistive sensor and a