Page 155 - Read Online
P. 155
Arab Hassani. Soft Sci 2023;3:31 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.23 Page 3 of 33
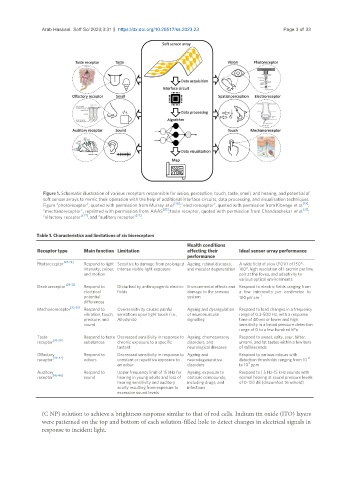
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of various receptors responsible for vision, perception, touch, taste, smell, and hearing, and potential of
soft sensor arrays to mimic their operation with the help of additional interface circuits, data processing, and visualisation techniques.
Figure “photoreceptor”, quoted with permission from Murray et al. [18] ; “electroreceptor”, quoted with permission from Kibenge et al. [19] ;
“mechanoreceptor”, reprinted with permission from AAAS [20] ; taste receptor, quoted with permission from Chandrashekar et al. [21] ;
“olfactory receptor” [22] , and “auditory receptor” [23] .
Table 1. Characteristics and limitations of six bioreceptors
Health conditions
Receptor type Main function Limitation affecting their Ideal sensor array performance
performance
Photoreceptor [24-28] Respond to light Sensitive to damage from prolonged Ageing, retinal diseases, A wide field of view (FOV) of 150°-
intensity, colour, intense visible light exposure and macular degeneration 160°, high resolution of 1 arcmin per line
and motion pair at the fovea, and adaptivity to
various optical environments
Electroreceptor [29-31] Respond to Disturbed by anthropogenic electric Environmental effects and Respond to electric fields ranging from
electrical fields damage to the sensory a few microvolts per centimetre to
potential system 100 μV·cm -1
differences
[32-35]
Mechanoreceptor Respond to Oversensitivity causes painful Ageing and dysregulation Respond to load changes in a frequency
vibration, touch, sensations upon light touch (i.e., of neuromuscular range of 0.3-500 Hz, with a response
pressure, and Allodynia) signalling time of 40 ms or lower and high
sound sensitivity in a broad pressure detection
range of 0 to a few hundred kPa
Taste Respond to taste Decreased sensitivity in response to Ageing, chemosensory Respond to sweet, salty, sour, bitter,
[36-39]
receptor substances chronic exposure to a specific disorders, and umami, and fat tastes within a few tens
tastant neurological diseases of milliseconds
Olfactory Respond to Decreased sensitivity in response to Ageing and Respond to various odours with
[40-42] -6
receptor odours constant or repetitive exposure to neurodegenerative detection thresholds ranging from 10
3
an odour disorders to 10 ppm
Auditory Respond to Upper frequency limit of 15 kHz for Ageing, exposure to Respond to 1.5 Hz-15 kHz sounds with
receptor [43-46] sound hearing in young adults and loss of ototoxic compounds, normal hearing at sound pressure levels
hearing sensitivity and auditory including drugs, and of 0-120 dB (discomfort threshold)
acuity resulting from exposure to infections
excessive sound levels
(C NP) solution to achieve a brightness response similar to that of rod cells. Indium tin oxide (ITO) layers
were patterned on the top and bottom of each solution-filled hole to detect changes in electrical signals in
response to incident light.