Page 193 - Read Online
P. 193
Nam et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:28 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.19 Page 17 of 35
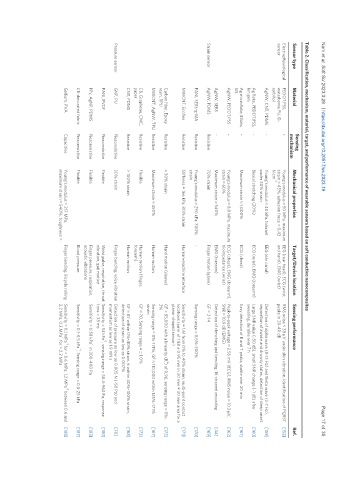
Table 2. Classification, mechanism, material, target, and performance of wearable sensors based on soft conductive nanocomposites
Sensing
Sensor type Material Mechanical properties Target/Device location Sensing performance Ref.
mechanism
Electrophysiological PEDOT:PSS, - Young’s modulus ≈ 50 MPa, maximum EEG (rear head), ECG (wrist RMS noise < 38 μV under skin vibration, Identification of PQRST [152]
sensor waterborne PU, D- strain = 43%, adhesion force = 0.43 and hand), EMG (wrist) peaks in 20-40 dB
-1
sorbitol N·cm
AgNW, CNT, PDMS - Young’s modulus ≈ 40 kPa, tolerant EEG (ear canal) Detection of alpha wave (8-13 Hz) and theta wave (3-7 Hz), [158]
under 30% strain separation of awake and drowsy states, detection of sleep onset
Ag flake, PEDOT:PSS, - Biaxial stretching (20%) ECG (wrist), EMG (forearm) Large SNR value (~50 dB), small SNR change (~1 dB) after [160]
Ion gels sweating, durable over 7 h
Ag microflake, EGaIn, - Maximum strain ≈ 1,000% ECG (chest) Easy detection of R and T peaks, stable over 20 min [161]
SIS
AgNW, PEDOT:PSS - Young’s modulus ≈ 8.8 MPa, maximum ECG (chest), EMG (forearm), Peak-to-peak voltage ≈ 2.56 mV (ECG), RMS noise ≈ 10.3 μV, [162]
strain ≈ 60% bioimpedance (wrist) SNR ≈ 10.9 dB (EMG)
AgNW, SEBS - Maximum strain ≈ 540% EMG (forearm) Detection of clenching and bending, 16-channel recording [44]
Strain sensor AgNW, PDMS Resistive 70% strain Finger motion (glove) GF = 2-14 [169]
PANI, SEBS-g-MA Resistive Young’s modulus ≈ 290 kPa, 300% - Sensing range = 0.5%-300% [170]
strain
MWCNT, Ecoflex Resistive Stiffness = 166 kPa, 80% strain Human-machine interface Sensitivity = 1.61 from 0% to 40% strain, multi-point contact [171]
locations (error of 1.88 ± 0.95 mm in 30 mm × 30 mm area for a
planar-shaped sensor)
2
Carbon fiber, Epoxy Resistive > 30% strain Hand motion (sleeve) GF > 85,000 with a linearity (R ) of 0.96, sensing range = 0%- [172]
resin, TPU 3%
MWCNT, AgNW, TPU Resistive Maximum strain ≈ 450% Human motion Sensing range = 0%-171%, GF ≈ 110,000 within 135%-171% [167]
strain
CB, Graphene, CMC, Resistive Flexible Human motion (finger, GF ≈ 70, Sensing range = ± 1.0% [173]
paper forearm)
CNT, PDMS Resistive > 100% strain Human motion GF ≈ 87 within 0%-40% strain, 6 within 40%-100% strain, [168]
detection of strain as low as 0.007%
Pressure sensor GNP, PU Piezoresistive 30% strain Finger bending, voice vibration Detection of pressure as low as 0.005 N (~50 Pa) and [70]
momentum as low as 1.9 mN·s
-1
PANI, PVDF Piezoresistive Flexible Wrist pulse, respiration, throat Sensitivity = 53 kPa , sensing range = 58.4-960 Pa, response [180]
vibration, gait motion time = 38 ms
-1
PPy, AgNP, PDMS Piezoresistive Flexible Finger pressure, respiration, Sensitivity = 0.58 kPa in 300-400 Pa [183]
acoustic vibrations
-1
CB-decorated fabric Piezoresistive Flexible Blood pressure Sensitivity = 0.1-0.5 kPa , Sensing range = 0.5-25 kPa [187]
-1 -1
Gallium, PVA Capacitive Young’s modulus = 217 MPa, Finger bending, Bicycle rolling Sensitivity = 0.1 MPa for < 0.6 MPa, 1.2 MPa between 0.6 and [188]
-1
maximum strain ≈ 540%, toughness = 2.2 MPa, 0.2 MPa for > 2.2 MPa