Page 181 - Read Online
P. 181
Nam et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:28 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.19 Page 5 of 35
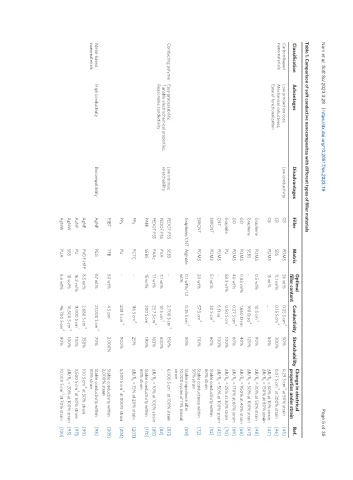
Table 1. Comparison of soft conductive nanocomposites with different types of filler materials
Optimal Change in electrical
Classification Advantages Disadvantages Filler Matrix Conductivity Stretchability Ref.
filler content properties under strain
-1 -1
Carbon-based Low production cost; Low conductivity CB PDMS 26 wt% 0.25 S·cm 50% 0.29 S·cm at 50% strain [45]
nanomaterials Mechanical robustness; CB SBS 11.1 vol% 0.15 S·cm -1 300% 0.07 S·cm at 300% strain [46]
-1
Ease of functionalization
CB PDMS 15 wt% _ 80% ΔR/R = 50% at 10% strain, [47]
0
ΔR/R = 150% at 80% strain
0
Graphene PDMS 0.5 wt% 10 S·cm -1 90% ΔR/R = 30% at 50% strain [48]
0
-1
Graphene SEBS - 100 Ω·sq 120% ΔR/R = 50% at 100% strain [67]
0
GO PDMS 0.83 vol% 1,660 Ω·cm 40% ΔR/R = 950% at 40% strain [68]
0
GO PDMS 40 wt% 0.27 S·cm -1 60% ΔR/R = 170% at 60% strain [69]
0
-1
Graphite PU 83.3 wt% 0.50 S·cm 100% ΔR/R = 25% at 30% strain [70]
0
-1
CNT PDMS - 6 Ω·sq 100% ΔR/R = 50% at 100% strain [43]
0
SWCNT PDMS 5.1 wt% 30 S·cm -1 60% Stable conductivity within [52]
60% strain
SWCNT PDMS 20 wt% 57 S·cm -1 110% Stable conductance within [72]
50% strain
Graphene/CNT Alginate 0.1 wt%/1.2 0.35 S·cm -1 50% Stable impedance after [59]
wt% 10,000 cycles of 11% biaxial
strain
-1 -1
Conducting polymer Easy processability; Low intrinsic PEDOT:PSS SEBS - 2,700 S·cm 150% 6,000 S·cm at 100% strain [87]
Tunable electrochemical properties; stretchability PEDOT:PSS PVA 7.1 wt% 10 S·cm -1 600% - [83]
Reasonable conductivity
PEDOT:PSS PAAc 1.1 wt% 23.7 S·cm -1 163% ΔR/R = 10% at 100% strain [85]
0
-1
PANI SEBS 15 vol% 200 S·cm 180% Stable conductivity within [170]
60% strain
-1
PPy PCTC - 116 S·cm 25% ΔR/R = 15% at 20% strain [203]
0
-1 -1
PPy PU - 238 S·cm 900% 5,300 S·cm at 800% strain [204]
-1
P3BT TFB 50 wt% 4 S·cm 2,000% Stable conductivity within [205]
2,000% strain
Metal-based High conductivity Biocompatibility AgNP PEG 67 wt% 21,000 S·cm -1 70% Stable conductivity within [98]
nanomaterials 50% strain
-1
AgNP PVDF-HFP 8.5 wt% 2,680 S·cm -1 350% 100 S·cm at 50% strain [99]
-1 -1
AuNP PU 16.2 vol% 11,000 S·cm 110% 3,500 S·cm at 60% strain [97]
AgNW SBS 18 vol% 10,500 S·cm -1 100% ΔR/R = 20% at 100% strain [93]
0
-1 -1
AgNW PUA 6.6 wt% 46,700 S·cm 80% 10,000 S·cm at 70% strain [100]