Page 130 - Read Online
P. 130
Page 12 of 19 Kim et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:18 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.08
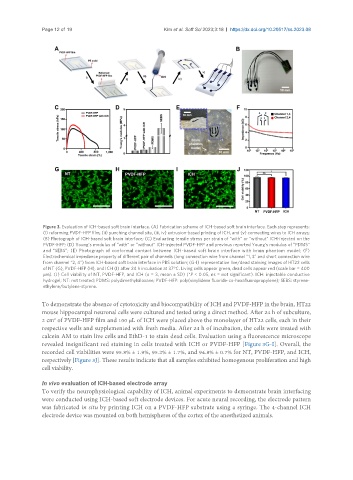
Figure 3. Evaluation of ICH-based soft brain interface. (A) Fabrication scheme of ICH-based soft brain interface. Each step represents:
(i) reforming PVDF-HFP film, (ii) punching channel site, (iii, iv) extrusion-based printing of ICH, and (v) connecting wires to ICH arrays;
(B) Photograph of ICH-based soft brain interface; (C) Evaluating tensile stress per strain of “with” or “without” ICH-injected on the
PVDF-HFP; (D) Young’s modulus of “with” or “without” ICH-injected PVDF-HFP and previous reported Young’s modulus of “PDMS”
and “SEBS”; (E) Photograph of conformal contact between ICH-based soft brain interface with brain phantom model; (F)
Electrochemical impedance property of different pair of channels (long connection wire from channel “1, 3” and short connection wire
from channel “2, 4”) from ICH-based soft brain interface in PBS solution; (G-I) representative live/dead staining images of HT22 cells
of NT (G), PVDF-HFP (H), and ICH (I) after 24 h incubation at 37°C. Living cells appear green, dead cells appear red (scale bar = 400
μm). (J) Cell viability of NT, PVDF-HFP, and ICH (n = 3, mean ± SD) (*P < 0.05, ns = not significant). ICH: injectable conductive
hydrogel; NT: not treated; PDMS: polydimethylsiloxane; PVDF-HFP: poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene); SEBS: styrene-
ethylene/butylene-styrene.
To demonstrate the absence of cytotoxicity and biocompatibility of ICH and PVDF-HFP in the brain, HT22
mouse hippocampal neuronal cells were cultured and tested using a direct method. After 24 h of subculture,
2 cm of PVDF-HFP film and 100 μL of ICH were placed above the monolayer of HT22 cells, each in their
2
respective wells and supplemented with fresh media. After 24 h of incubation, the cells were treated with
calcein AM to stain live cells and EthD-1 to stain dead cells. Evaluation using a fluorescence microscope
revealed insignificant red staining in cells treated with ICH or PVDF-HFP [Figure 3G-I]. Overall, the
recorded cell viabilities were 95.8% ± 1.9%, 95.2% ± 1.7%, and 94.8% ± 0.7% for NT, PVDF-HFP, and ICH,
respectively [Figure 3J]. These results indicate that all samples exhibited homogenous proliferation and high
cell viability.
In vivo evaluation of ICH-based electrode array
To verify the neurophysiological capability of ICH, animal experiments to demonstrate brain interfacing
were conducted using ICH-based soft electrode devices. For acute neural recording, the electrode pattern
was fabricated in situ by printing ICH on a PVDF-HFP substrate using a syringe. The 4-channel ICH
electrode device was mounted on both hemispheres of the cortex of the anesthetized animals.