Page 64 - Read Online
P. 64
Aguiar. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2024;3:13 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.56 Page 5 of 29
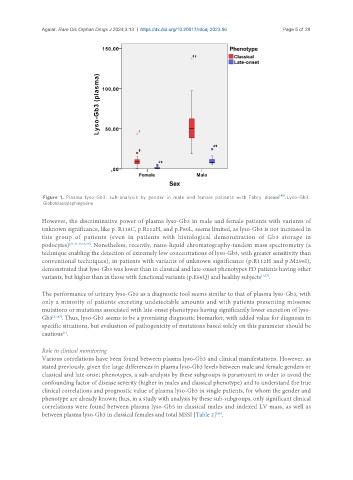
Figure 1. Plasma lyso-Gb3: sub-analysis by gender in male and female patients with Fabry disease [46] . Lyso-Gb3:
Globotriaosylsphingosine.
However, the discriminative power of plasma lyso-Gb3 in male and female patients with variants of
unknown significance, like p. R118C, p.R112H, and p.P60L, seems limited, as lyso-Gb3 is not increased in
this group of patients (even in patients with histological demonstration of Gb3 storage in
podocytes) [31,41,45,55,56] . Nonetheless, recently, nano-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (a
technique enabling the detection of extremely low concentrations of lyso-Gb3, with greater sensitivity than
conventional techniques), in patients with variants of unknown significance (p.R112H and p.M296I),
demonstrated that lyso-Gb3 was lower than in classical and late-onset phenotypes FD patients having other
variants, but higher than in those with functional variants (p.E66Q) and healthy subjects [1,57] .
The performance of urinary lyso-Gb3 as a diagnostic tool seems similar to that of plasma lyso-Gb3, with
only a minority of patients excreting undetectable amounts and with patients presenting missense
mutations or mutations associated with late-onset phenotypes having significantly lower excretion of lyso-
Gb3 [33,47] . Thus, lyso-Gb3 seems to be a promising diagnostic biomarker, with added value for diagnosis in
specific situations, but evaluation of pathogenicity of mutations based solely on this parameter should be
cautious .
[1]
Role in clinical monitoring
Various correlations have been found between plasma lyso-Gb3 and clinical manifestations. However, as
stated previously, given the large differences in plasma lyso-Gb3 levels between male and female genders or
classical and late-onset phenotypes, a sub-analysis by these subgroups is paramount in order to avoid the
confounding factor of disease severity (higher in males and classical phenotype) and to understand the true
clinical correlations and prognostic value of plasma lyso-Gb3 in single patients, for whom the gender and
phenotype are already known; thus, in a study with analysis by these sub-subgroups, only significant clinical
correlations were found between plasma lyso-Gb3 in classical males and indexed LV mass, as well as
between plasma lyso-Gb3 in classical females and total MSSI [Table 2] .
[46]