Page 802 - Read Online
P. 802
Page 6 of 12 Bair et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:68 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.74
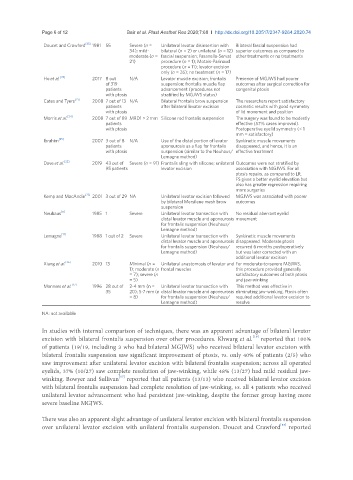
Doucet and Crawford [33] 1981 55 Severe (n = Unilateral levator disinsertion with Bilateral fascial suspension had
34); mild- bilateral (n = 2) or unilateral (n = 12) superior outcomes as compared to
moderate (n = fascial suspension; Fasanella-Servat other treatments or no treatments
21) procedure (n = 1); Motais-Parinaud
procedure (n = 11); levator excision
only (n = 26); no treatment (n = 17)
Ho et al. [24] 2017 8 out N/A Levator muscle excision; frontalis Presence of MGJWS had poorer
of 319 suspension; frontalis muscle flap outcomes after surgical correction for
patients advancement (procedures not congenital ptosis
with ptosis stratified by MGJWS status)
Cates and Tyers [21] 2008 7 out of 13 N/A Bilateral frontalis brow suspension The researchers report satisfactory
patients after bilateral levator excision cosmetic results with good symmetry
with ptosis of lid movement and position
Morris et al. [34] 2008 7 out of 89 MRD1 > 2 mm Silicone rod frontalis suspension The surgery was found to be modestly
patients effective (57% cases improved).
with ptosis Postoperative eyelid symmetry (< 1
mm = satisfactory)
Ibrahim [35] 2007 3 out of 8 N/A Use of the distal portion of levator Synkinetic muscle movements
patients aponeurosis as a flap for frontalis disappeared, and hence, it is an
with ptosis suspension (similar to the Neuhaus/ effective treatment
Lemagne method)
Dave et al. [22] 2019 43 out of Severe (n = 91) Frontalis sling with silicone; unilateral Outcomes were not stratified by
95 patients levator excision association with MGJWS. For all
ptosis repairs, as compared to LR,
FS gives a better eyelid elevation but
also has greater regression requiring
more surgeries
Kemp and MacAndie [23] 2001 3 out of 29 NA Unilateral levator excision followed MGJWS was associated with poorer
by bilateral Mersilene mesh brow outcomes
suspension
Neuhaus [11] 1985 1 Severe Unilateral levator transection with No residual aberrant eyelid
distal levator muscle and aponeurosis movement
for frontalis suspension (Neuhaus/
Lemagne method)
Lemagne [17] 1988 1 out of 2 Severe Unilateral levator transection with Synkinetic muscle movements
distal levator muscle and aponeurosis disappeared. Moderate ptosis
for frontalis suspension (Neuhaus/ recurred 6 months postoperatively
Lemagne method) but was later corrected with an
additional levator excision
Xiang et al. [36] 2010 13 Minimal (n = Unilateral anastomosis of levator and For moderate-to-severe MGJWS,
1); moderate (n frontal muscles this procedure provided generally
= 7); severe (n satisfactory outcomes of both ptosis
= 5) and jaw-winking
Manners et al. [37] 1996 28 out of 2-4 mm (n = Unilateral levator transection with This method was effective in
35 20); 5-7 mm (n distal levator muscle and aponeurosis eliminating jaw-winking. Ptosis often
= 8) for frontalis suspension (Neuhaus/ required additional levator excision to
Lemagne method) resolve
NA: not available
In studies with internal comparison of techniques, there was an apparent advantage of bilateral levator
[19]
excision with bilateral frontalis suspension over other procedures. Khwarg et al. reported that 100%
of patients (19/19, including 3 who had bilateral MGJWS) who received bilateral levator excision with
bilateral frontalis suspension saw significant improvement of ptosis, vs. only 40% of patients (2/5) who
saw improvement after unilateral levator excision with bilateral frontalis suspension; across all operated
eyelids, 37% (10/27) saw complete resolution of jaw-winking, while 48% (13/27) had mild residual jaw-
[17]
winking. Bowyer and Sullivan reported that all patients (13/13) who received bilateral levator excision
with bilateral frontalis suspension had complete resolution of jaw-winking, vs. all 4 patients who received
unilateral levator advancement who had persistent jaw-winking, despite the former group having more
severe baseline MGJWS.
There was also an apparent slight advantage of unilateral levator excision with bilateral frontalis suspension
[33]
over unilateral levator excision with unilateral frontalis suspension. Doucet and Crawford reported