Page 116 - Read Online
P. 116
Muñoz-Jimenez et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.04 Page 3 of 5
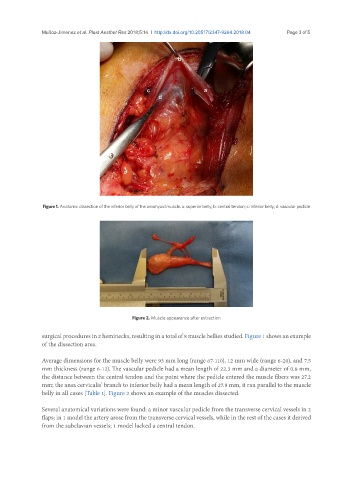
Figure 1. Anatomic dissection of the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle. a: superior belly; b: central tendon; c: inferior belly; d: vascular pedicle
Figure 2. Muscle appearance after extraction
surgical procedures in 2 heminecks, resulting in a total of 8 muscle bellies studied. Figure 1 shows an example
of the dissection area.
Average dimensions for the muscle belly were 93 mm long (range 67-110), 12 mm wide (range 6-20), and 7.5
mm thickness (range 6-12). The vascular pedicle had a mean length of 22.3 mm and a diameter of 0.8 mm,
the distance between the central tendon and the point where the pedicle entered the muscle fibers was 27.2
mm; the ansa cervicalis’ branch to inferior belly had a mean length of 27.8 mm, it ran parallel to the muscle
belly in all cases [Table 1]. Figure 2 shows an example of the muscles dissected.
Several anatomical variations were found: a minor vascular pedicle from the transverse cervical vessels in 2
flaps; in 1 model the artery arose from the transverse cervical vessels, while in the rest of the cases it derived
from the subclavian vessels; 1 model lacked a central tendon.