Page 112 - Read Online
P. 112
Page 4 of 5 Agrawal et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:13 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.17
A B
C D
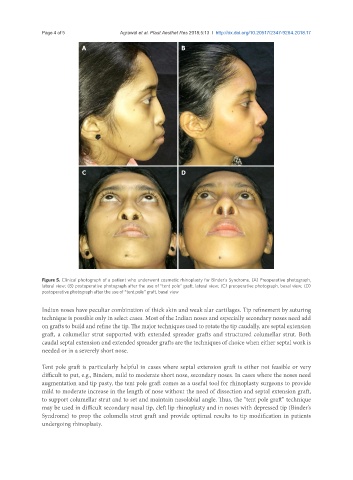
Figure 5. Clinical photograph of a patient who underwent cosmetic rhinoplasty for Binder’s Syndrome. (A) Preoperative photograph,
lateral view; (B) postoperative photograph after the use of “tent pole” graft, lateral view; (C) preoperative photograph, basal view; (D)
postoperative photograph after the use of “tent pole” graft, basal view
Indian noses have peculiar combination of thick skin and weak alar cartilages. Tip refinement by suturing
technique is possible only in select cases. Most of the Indian noses and especially secondary noses need add
on grafts to build and refine the tip. The major techniques used to rotate the tip caudally, are septal extension
graft, a columellar strut supported with extended spreader grafts and structured columellar strut. Both
caudal septal extension and extended spreader grafts are the techniques of choice when either septal work is
needed or in a severely short nose.
Tent pole graft is particularly helpful in cases where septal extension graft is either not feasible or very
difficult to put, e.g., Binders, mild to moderate short nose, secondary noses. In cases where the noses need
augmentation and tip pasty, the tent pole graft comes as a useful tool for rhinoplasty surgeons to provide
mild to moderate increase in the length of nose without the need of dissection and septal extension graft,
to support columellar strut and to set and maintain nasolabial angle. Thus, the “tent pole graft” technique
may be used in difficult secondary nasal tip, cleft lip rhinoplasty and in noses with depressed tip (Binder’s
Syndrome) to prop the columella strut graft and provide optimal results to tip modification in patients
undergoing rhinoplasty.