Page 193 - Read Online
P. 193
Horch et al. Towards the future of plastic surgery
concept and rendering plastic surgery as a problem and the size of the defect as well as on the vascular
solving discipline within the concert of all medical situation of the recipient site [13] . In diabetic foot ulcers
specialities. It has been shown that such modern for instance the indications for local flaps are rather
interdisciplinary concepts contribute significantly to limited. It also has to be taken into account that any
improving the patient´s quality of life. local flap does not only cause a donor site defect
but also may further deteriorate the vascular supply
As an example one can look at the salvage of of the distal extremity. In experimental studies the
hypovascularized wounds in the lower extremity, that is potential role of neo-angiogenesis at the non-ischemic/
made possible by transferring well vascularized tissue ischemic interfaces are key to the biological healing
utilizing microsurgery. This concept utilizes the surgical process. Such interfaces occur after transfer of free
induction of angiogenesis for the treatment of chronic, vascularized flaps into ischemic wounds [14,15] . Due to
poorly vascularized wounds, such as in diabetic the standardization of microsurgery the age of patients
ulcers and ulcers following arteriosclerotic disease [1-5] . seems to be no hindrance to become eligible for free
Autologous venous bypass grafts can be used as a flap transfers to the lower extremity. A correlation
prolongation or as arterio-venous loops to allow for between flap loss and increased risk factors and age
a distal free flap connection even in the absence was not found in the elderly population so far [16-18] .
of appropriate local vessels, before amputation is
necessitated. We have been using this concept for We have gained experience with more than 100
more than 20 years now and have investigated a larger patients who received a bypass or an av-loop (primarily
cohort of such selected patients who needed bypasses or staged) along with a free flap and we could show
and microsurgical free flaps. We have therefore that weighed against the gain in quality of life the donor
assessed and advocated an algorithm based on our site morbidity is comparatively low and acceptable.
results and from current literature data [6-11] . Nevertheless a consequent patient selection and
a thorough planning can help to keep the rate of
complications low.
Perforator flaps have significantly contributed to a
further reduction in donor sit morbidity when compared
to myocutaneous or muscle flaps. Perforator flaps It is the daily routine of plastic surgeons to deal with
have been advocated to be another soft tissue choice
for all zones of the lower extremity, recognizing that
donor site function preservation is their major asset
because in such perforator flaps no muscle needs to
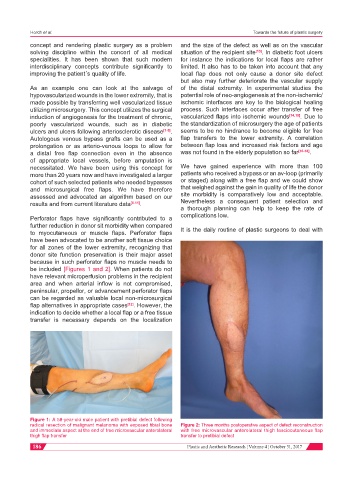
be included [Figures 1 and 2]. When patients do not
have relevant microperfusion problems in the recipient
area and when arterial inflow is not compromised,
peninsular, propellor, or advancement perforator flaps
can be regarded as valuable local non-microsurgical
flap alternatives in appropriate cases [12] . However, the
indication to decide whether a local flap or a free tissue
transfer is necessary depends on the localization
Figure 1: A 58-year-old male patient with pretibial defect following
radical resection of malignant melanoma with exposed tibial bone Figure 2: Three months postoperative aspect of defect reconstruction
and immediate aspect at the end of free microvascular anterolateral with free microvascular anterolateral thigh fasciocutaneous flap
thigh flap transfer transfer to pretibial defect
186 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ October 31, 2017