Page 153 - Read Online
P. 153
Fariña et al. Skeletal anchorage for rigid external distractor
Table 1: Patient distribution according to age, gender, diagnosis, type of osteotomy, amount of distraction, relapse,
and follow-up
Patients Age Overjet before Type of Days of Overjet a year after Relapse Follow-up
No. (years) Gender Diagnosis surgery osteotomy activation (mm) distraction (mm) (mm) (months)
1 9 M Crouzon Sd -20 Le Fort III 30 +3 0 15
2 15 F Severe class III -16 Le Fort III 25 +2 0 55
maloclussion
3 17 M Crouzon Sd -13 Le Fort III 24 +3 0 24
4 25 M Crouzon Sd -16 Le Fort III 22 +3 0 36
5 9 M CLP -15 Le Fort III 25 -5 5 60
6 20 F CLP -12 Le Fort I 20 +2 0 30
7 18 M Crouzon Sd -25 Le Fort III 30 +2 0 36
8 21 F CLP -14 Le Fort I 25 +3 0 36
9 24 M CLP -12 Le Fort I 20 +2 0 30
Average 17.5 -15.8 24.5 1.6 0.55 35.7
CLP: cleft lip and palate; Sd: syndrome
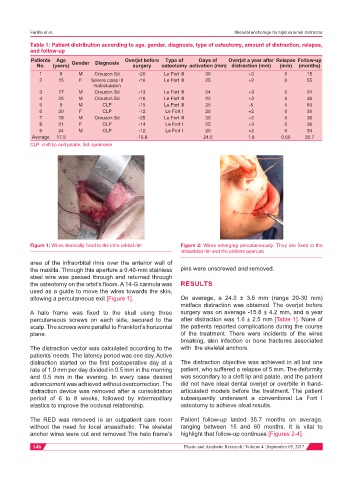
Figure 1: Wires skeletally fixed to the infra orbital rim Figure 2: Wires emerging percutaneously. They are fixed to the
infraorbital rim and the piriform aperture
area of the infraorbital rims over the anterior wall of
the maxilla. Through this aperture a 0.40-mm stainless pins were unscrewed and removed.
steel wire was passed through and returned through
the osteotomy on the orbit’s floors. A 14-G cannula was RESULTS
used as a guide to move the wires towards the skin,
allowing a percutaneous exit [Figure 1]. On average, a 24.0 ± 3.6 mm (range 20-30 mm)
midface distraction was obtained. The overjet before
A halo frame was fixed to the skull using three surgery was on average -15.8 ± 4.2 mm, and a year
percutaneous screws on each side, secured to the after distraction was 1.6 ± 2.5 mm [Table 1]. None of
scalp. The screws were parallel to Frankfort’s horizontal the patients reported complications during the course
plane. of the treatment. There were incidents of the wires
breaking, skin infection or bone fractures associated
The distraction vector was calculated according to the with the skeletal anchors.
patients’ needs. The latency period was one day. Active
distraction started on the first postoperative day at a The distraction objective was achieved in all but one
rate of 1.0 mm per day divided in 0.5 mm in the morning patient, who suffered a relapse of 5 mm. The deformity
and 0.5 mm in the evening. In every case desired was secondary to a cleft lip and palate, and the patient
advancement was achieved without overcorrection. The did not have ideal dental overjet or overbite in hand-
distraction device was removed after a consolidation articulated models before the treatment. The patient
period of 6 to 8 weeks, followed by intermaxillary subsequently underwent a conventional Le Fort I
elastics to improve the occlusal relationship. osteotomy to achieve ideal results.
The RED was removed in an outpatient care room Patient follow-up lasted 35.7 months on average,
without the need for local anaesthetic. The skeletal ranging between 15 and 60 months. It is vital to
anchor wires were cut and removed The halo frame’s highlight that follow-up continues [Figures 2-4].
146 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ September 05, 2017