Page 287 - Read Online
P. 287
authors’ experience of JFT in the management of chronic was used. In Group 2, once the tissue cultures became
wounds. negative, the wound was covered with a skin graft or
flap.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
RESULTS
This is a retrospective study of patients with chronic
nonhealing wounds in whom JFT was used in the In our study cohort (n = 18 patients), the age
Department of Plastic Surgery, Jawaharlal Institute of the patients ranged from 23 years to 75 years
of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, (mean: 49.32 years). In Group 1, the mean age was
Pondicherry, India from November 2013 to October 2014. 55.2 years and 46.5 years in Group 2. There were more
Patients of all age groups and both genders with chronic men than women with a ratio of 2.4:1. The most common
nonhealing wounds (> 3 months duration) of different site for chronic wounds was the lower extremity. The
etiologies which had undergone surgical debridement most common etiology was a diabetic ulcer, followed
but were not ready for reconstruction due to debris and by a posttraumatic region of excoriation. The size of the
infection were included in the study. Eighteen patients wounds varied from 3 cm × 2 cm to 20 cm × 10 cm. The
matched the inclusion criteria. Informed consent was mean Bates‑Jansen wound score was 33 ± 1 in Group 1
obtained. Details including age, gender, etiology, and 36 ± 1 in Group 2. The mean wound area in Group 1
duration of wound, site, size, co‑morbid factors, type of was 42.6 cm and 55.4 cm in Group 2. In both groups, all
2
2
organism grown in tissue culture prior to JFT, duration wounds were culture positive for polymicrobial growth.
to negative cultures following JFT, and duration until In both groups, the most common organism cultured was
wound healing were recorded in the study proforma. Pseudomonas aeruginosa followed by Staphylococcus aureus.
The wound score was documented using the Bates In Group 1, tissue cultures became negative after a mean
Jansen Wound Assessment Tool. Wound measurements duration of 2.17 weeks, whereas in Group 2, tissue cultures
[4]
were recorded by Digital Planimetry using Image‑J became negative after a mean duration of 2.34 weeks.
Software (National Institutes of Health). Wound score On combining of both groups (18 patients), the wounds
[5]
and measurements were recorded at each dressing required 2.25 weeks to become culture negative. The
changes. Patients were evaluated for medical clearance mean number of JFT sessions in Group 1 was 3.67, while
for anesthesia. Wound tissue cultures were sent prior to the mean number of JFT sessions in Group 2 was 4.58.
beginning JFT and weekly thereafter. JFT hydrotherapy In Group 1 (6 patients) managed by JFT alone, the mean
and dressing changes were performed when the wound duration to complete healing was 4 weeks. In Group 2
dressings were noted to be soaked. No systemic (12 patients) managed by JFT and split skin graft/flap, the
antibiotic therapy was required in any of the cases. Only mean duration to complete healing was 3.25 weeks [Tables
saline moist dressings were used. JFT hydrotherapy was 1 and 2, Figures 3‑5]. Only group 2 received flap or graft.
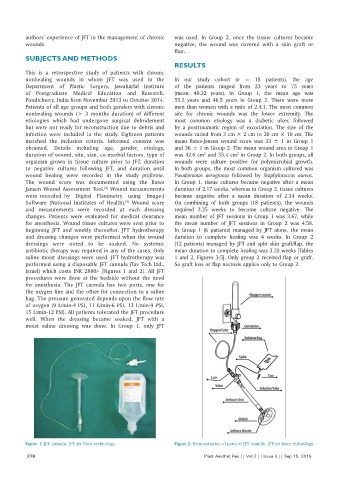
performed using a disposable JFT cannula (Tav Tech Ltd., So graft loss or flap necrosis applies only to Group 2.
Israel) which costs INR 2880/‑ [Figures 1 and 2]. All JFT
procedures were done at the bedside without the need
for anesthesia. The JFT cannula has two ports, one for
the oxygen line and the other for connection to a saline
bag. The pressure generated depends upon the flow rate
of oxygen (9 L/min‑4 PSI, 11 L/min‑6 PSI, 13 L/min‑9 PSI,
15 L/min‑12 PSI). All patients tolerated the JFT procedure
well. When the dressing became soaked, JFT with a
moist saline dressing was done. In Group 1, only JFT
Figure 1: JET cannula. JFT: jet force technology Figure 2: Demonstration of parts of JET cannula. JFT: jet force technology
278 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 5 || Sep 15, 2015