Page 156 - Read Online
P. 156
another surgical incision. Its anatomy is more constant.
Perforators are almost always present, and their pedicles
are of sufficient length (average of 8 cm). As a perforator
flap, a thinner and more pliable flap can be obtained,
removing a variable portion of muscular tissue and leaving
only a cuff around the pedicle. Therefore, it can be used
for almost the same indications of ALT flap. [2-5]
The published reports of TFL flap in groin reconstruction
following inguinal node dissection have enumerated
partial flap necrosis, distal tip necrosis, flap infection and
lymphedema as various complications. [2,3,5]
In our case, we found TFL perforator flap to be the
best choice because it allowed maintaining the same
reconstructive plan made with the ALT flap.
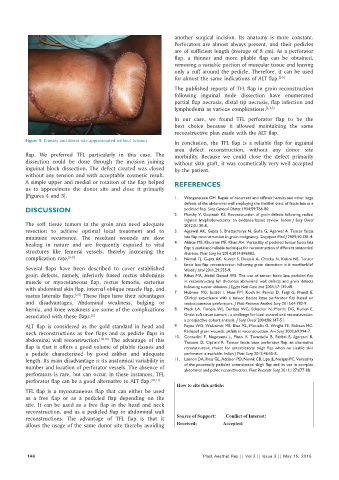
Figure 5: Primary and donor site approximated without tension In conclusion, the TFL flap is a reliable flap for inguinal
area defect reconstruction, without any donor site
flap. We preferred TFL particularly in this case. The morbidity. Because we could close the defect primarily
dissection could be done through the incision joining without skin graft, it was cosmetically very well accepted
inguinal block dissection. The defect created was closed by the patient.
without any tension and with acceptable cosmetic result.
A simple upper and medial or rotation of the flap helped REFERENCES
us to approximate the donor site and close it primarily
[Figures 4 and 5]. 1. Wangensteen OH. Repair of recurrent and difficult hernias and other large
defects of the abdominal wall employing the iliotibial tract of fascia lata as a
DISCUSSION pedicled flap. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1934;59:766‑80.
2. Murthy V, Gopinath KS. Reconstruction of groin defects following radical
inguinal lymphadenectomy: an evidence based review. Indian J Surg Oncol
The soft tissue tumors in the groin area need adequate 2012;3:130‑8.
resection to achieve optimal local treatment and to 3. Agarwal AK, Gupta S, Bhattacharya N, Guha G, Agarwal A. Tensor fascia
minimize recurrence. The resultant wounds are slow lata flap reconstruction in groin malignancy. Singapore Med J 2009;50:781‑4.
healing in nature and are frequently exposed to vital 4. Akhtar MS, Khurram MF, Khan AH. Versatility of pedicled tensor fascia lata
structures like femoral vessels, thereby increasing the flap: a useful and reliable technique for reconstruction of different anatomical
districts. Plast Surg Int 2014;2014:846082.
complication rate. [6-9] 5. Nirmal TJ, Gupta AK, Kumar S, Devasia A, Chacko N, Kekre NS. Tensor
fascia lata flap reconstruction following groin dissection: is it worthwhile?
Several flaps have been described to cover established World J Urol 2011;29:555‑9.
groin defects, namely, inferiorly based rectus abdominis 6. Rifaat MA, Abdel Gawad WS. The use of tensor fascia lata pedicled flap
muscle or myocutaneous flap, rectus femoris, sartorius in reconstructing full thickness abdominal wall defects and groin defects
with abdominal skin flap, internal oblique muscle flap, and following tumor ablation. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 2005;17:139‑48.
vastus lateralis flaps. [2-5] These flaps have their advantages 7. Hubmer MG, Justich I, Haas FM, Koch H, Parvizi D, Feigl G, Prandl E.
Clinical experience with a tensor fasciae latae perforator flap based on
and disadvantages. Abdominal weakness, bulging or septocutaneous perforators. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2011;64:782‑9.
hernia, and knee weakness are some of the complications 8. Mack LA, Temple WJ, DeHaas WG, Schachar N, Morris DG, Kurien E.
associated with these flaps. [2] Groin soft tissue tumors ‑ a challenge for local control and reconstruction:
a prospective cohort analysis. J Surg Oncol 2004;86:147‑51.
ALT flap is considered as the gold standard in head and 9. Payne WG, Walusimbi MS, Blue ML, Mosiello G, Wright TE, Robson MC.
neck reconstructions as free flaps and as pedicle flaps in Radiated groin wounds: pitfalls in reconstruction. Am Surg 2003;69:994‑7.
abdominal wall reconstruction. [10,11] The advantage of this 10. Contedini F, Negosanti L, Pinto V, Tavaniello B, Fabbri E, Sgarzani R,
Tassone D, Cipriani R. Tensor fascia latae perforator flap: an alternative
flap is that it offers a good volume of pliable tissues and reconstructive choice for anterolateral thigh flap when no sizable skin
a pedicle characterized by good caliber and adequate perforator is available. Indian J Plast Surg 2013;46:55‑8.
length. Its main disadvantage is its anatomical variability in 11. Lannon DA, Ross GL, Addison PD, Novak CB, Lipa JE, Neligan PC. Versatility
number and location of perforator vessels. The absence of of the proximally pedicled anterolateral thigh flap and its use in complex
abdominal and pelvic reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2011;127:677‑88.
perforators is rare, but can occur. In these instances, TFL
perforator flap can be a good alternative to ALT flap. [10,11]
How to cite this article: Jena A, Manilal B, Haranadh S, Patnayak R.
TFL flap is a myocutaneous flap that can either be used Use of tensor fascia lata flap for reconstruction of the defect created
as a free flap or as a pedicled flap depending on the following inguinal block dissection in a case of carcinoma penis:
site. It can be used as a free flap in the head and neck a case report and brief review of literature. Plast Aesthet Res
reconstruction, and as a pedicled flap in abdominal wall 2015;2:144-6.
reconstructions. The advantage of TFL flap is that it Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: None declared.
allows the usage of the same donor site thereby avoiding Received: 25-11-2014; Accepted: 13-02-2015
146 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 3 || May 15, 2015