Page 93 - Read Online
P. 93
DISCUSSION to the following formula: P = 2R × 3.14 = d × 3.14 (R:
radius = d/2). This measurement allowed us to determine
Either the DGA or SGA perfuse the medial femoral condyle. the outer diameter in noninflated arteries.
The current study evaluated the anatomical structures and Our study detected the DGA in 82.5% and the
variations of the DGA and SGA as well as their branches in SGA in 25% of the 40 specimens. Yamamoto
adult cadavers. One half of cadavers were studied in fresh et al. found the DGA in 89% and the SGA in 100% of the
[7]
condition to facilitate the evaluation of the perfusion area 19 specimens. Rahmanian-Schwarz et al. harvested the
[1]
of skin and bone.
DGA in 100% of the 21 specimens and Iorio et al. also
[16]
Prior studies have shown that the outer diameter of discovered the DGA in 100% of the 12 specimens. The
the artery from fresh frozen cadavers was maintained. difference between the studies is secondary to the number
While the diameter of arteries from cadavers preserved of specimens.
in formalin retracts and loses its shape, the perimeter of In the current study, the dominant vessels supplying the
the artery is maintained. We calculated the outer medial femoral condyle were the DGA in 82.5% of cases
[7]
diameter of the artery through its perimeter according
and the SGA in the DGA and 17.5% of cases. Van Dijck
et al. showed that in 70% of cases the DGA was dominant,
[6]
while in 21% of cases the SGA was the dominant vessel. In
9% of cases the DGA and SGA supplied the medial femoral
condyle equally. A comparison between the measurements
of the DGA in the current study and other studies is made
in Table 1.
Similar to previous studies, the current study
demonstrated that the DGA generally divides into 3
branches (63.7% of cases) or 2 branches (33.3% of cases).
In addition, the AB of the DGA or the SGA always
nourishes the periosteum of the medial femoral condyle.
These arteries have adequate diameter and length to
supply the medial femoral condylar flap. In the absence
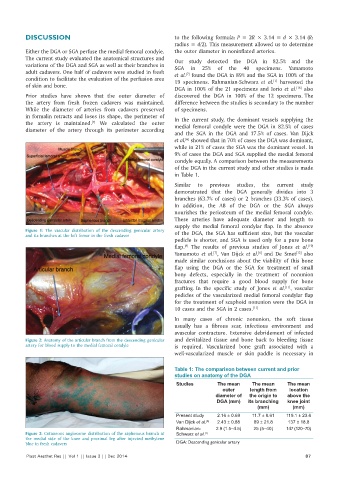
Figure 1: The vascular distribution of the descending genicular artery of the DGA, the SGA has sufficient size, but the vascular
and its branches at the left femur in the fresh cadaver
pedicle is shorter, and SGA is used only for a pure bone
[8]
flap. The results of previous studies of Jones et al.
[10]
[6]
[13]
Yamamoto et al. , Van Dijck et al. and De Smet also
[7]
made similar conclusions about the viability of this bone
flap using the DGA or the SGA for treatment of small
bony defects, especially in the treatment of nonunion
fractures that require a good blood supply for bone
grafting. In the specific study of Jones et al. , vascular
[11]
pedicles of the vascularized medial femoral condylar flap
for the treatment of scaphoid nonunion were the DGA in
10 cases and the SGA in 2 cases. [11]
In many cases of chronic nonunion, the soft tissue
usually has a fibrous scar, infectious environment and
avascular contracture. Extensive debridement of infected
Figure 2: Anatomy of the articular branch from the descending genicular and devitalized tissue and bone back to bleeding tissue
artery for blood supply to the medial femoral condyle is required. Vascularized bone graft associated with a
well-vascularized muscle or skin paddle is necessary in
Table 1: The comparison between current and prior
studies on anatomy of the DGA
Studies The mean The mean The mean
outer length from location
diameter of the origin to above the
DGA (mm) its branching knee joint
(mm) (mm)
Present study 2.16 ± 0.69 11.7 ± 8.61 119.1 ± 23.6
Van Dijck et al. [6] 2.43 ± 0.88 89 ± 21.8 137 ± 18.8
Rahmanian- 2.9 (1.5–4.5) 25 (5–40) 147 (120–70)
Figure 3: Cutaneous angiosome distribution of the saphenous branch at Schwarz et al. [1]
the medial side of the knee and proximal leg after injected methylene
blue in fresh cadavers DGA: Descending genicular artery
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 3 || Dec 2014 87