Page 93 - Read Online
P. 93
Page 10 of 16 Mataix et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:69 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.138
n
n
n
®
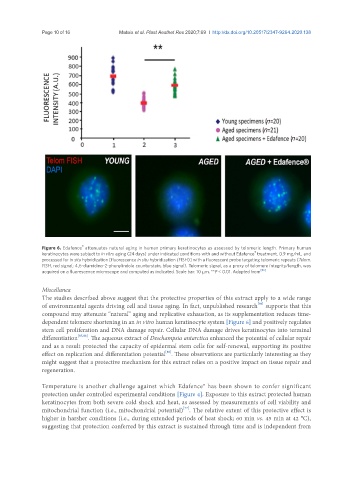
Figure 6. Edafence attenuates natural aging in human primary keratinocytes as assessed by telomeric length. Primary human
keratinocytes were subject to in vitro aging (24 days) under indicated conditions with and without Edafence treatment, 0.9 mg/mL, and
®
processed for in situ hybridization [fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)] with a fluorescent probe targeting telomeric repeats (Telom.
FISH, red signal; 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole counterstain, blue signal). Telomeric signal, as a proxy of telomere integrity/length, was
acquired on a fluorescence microscope and computed as indicated. Scale bar: 10 µm. **P < 0.01. Adapted from [86]
Miscellanea
The studies described above suggest that the protective properties of this extract apply to a wide range
of environmental agents driving cell and tissue aging. In fact, unpublished research supports that this
[86]
compound may attenuate “natural” aging and replicative exhaustion, as its supplementation reduces time-
dependent telomere shortening in an in vitro human keratinocyte system [Figure 6] and positively regulates
stem cell proliferation and DNA damage repair. Cellular DNA damage drives keratinocytes into terminal
differentiation [87,88] . The aqueous extract of Deschampsia antarctica enhanced the potential of cellular repair
and as a result protected the capacity of epidermal stem cells for self-renewal, supporting its positive
effect on replication and differentiation potential . These observations are particularly interesting as they
[86]
might suggest that a protective mechanism for this extract relies on a positive impact on tissue repair and
regeneration.
Temperature is another challenge against which Edafence® has been shown to confer significant
protection under controlled experimental conditions [Figure 4]. Exposure to this extract protected human
keratinocytes from both severe cold shock and heat, as assessed by measurements of cell viability and
[77]
mitochondrial function (i.e., mitochondrial potential) . The relative extent of this protective effect is
higher in harsher conditions (i.e., during extended periods of heat shock; 60 min vs. 45 min at 42 °C),
suggesting that protection conferred by this extract is sustained through time and is independent from