Page 91 - Read Online
P. 91
Page 8 of 16 Mataix et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:69 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.138
A
B
®
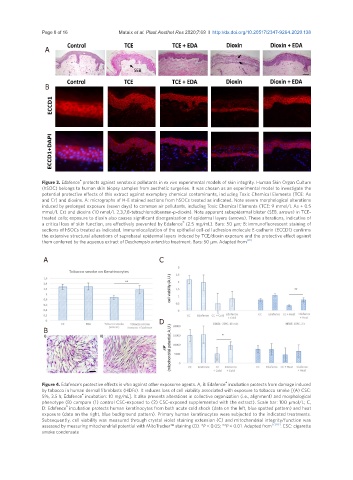
Figure 3. Edafence protects against xenotoxic pollutants in ex vivo experimental models of skin integrity. Human Skin Organ Culture
(hSOC) belongs to human skin biopsy samples from aesthetic surgeries. It was chosen as an experimental model to investigate the
potential protective effects of this extract against exemplary chemical contaminants, including Toxic Chemical Elements (TCE: As
and Cr) and dioxins. A: micrographs of H-E stained sections from hSOCs treated as indicated. Note severe morphological alterations
induced by prolonged exposure (seven days) to common air pollutants, including Toxic Chemical Elements (TCE: 9 mmol/L As + 0.5
mmol/L Cr) and dioxins (10 nmol/L 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzen-p-dioxin). Note apparent subepidermal blister (SEB, arrows) in TCE-
treated cells; exposure to dioxin also causes significant disorganization of epidermal layers (arrows). These alterations, indicative of
®
a critical loss of skin function, are effectively prevented by Edafence (2.5 mg/mL). Bars: 50 µm; B: immunofluorescent staining of
sections of hSOCs treated as indicated. Immunolocalization of the epithelial cell-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin (ECCD1) confirms
the extensive structural alterations of suprabasal epidermal layers induced by TCE/dioxin exposure and the protective effect against
them conferred by the aqueous extract of Deschampsia antarctica treatment. Bars: 50 µm. Adapted from [82]
A C
D
B
®
Figure 4. Edafence’s protective effects in vitro against other exposome agents. A, B: Edafence incubation protects from damage induced
by tobacco in human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs). It reduces loss of cell viability associated with exposure to tobacco smoke [(A) CSC:
®
5%, 3.5 h; Edafence incubation: 10 mg/mL]. It also prevents alterations in collective organization (i.e., alignment) and morphological
phenotype (B) compare (1) control CSC-exposed to (2) CSC-exposed supplemented with the extract). Scale bar: 100 µmol/L; C,
®
D: Edafence incubation protects human keratinocytes from both acute cold shock (data on the left, blue spotted pattern) and heat
exposure (data on the right, blue background pattern). Primary human keratinocytes were subjected to the indicated treatments.
Subsequently, cell viability was measured through crystal violet staining extension (C) and mitochondrial integrity/function was
assessed by measuring mitochondrial potential with MitoTracker™ staining (D). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Adapted from [77,83] . CSC: cigarette
smoke condensate