Page 92 - Read Online
P. 92
Mataix et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:69 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.138 Page 9 of 16
®
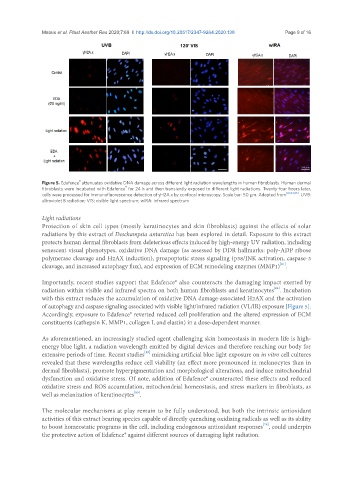
Figure 5. Edafence attenuates oxidative DNA damage across different light radiation wavelengths in human fibroblasts. Human dermal
®
fibroblasts were incubated with Edafence for 24 h and then transiently exposed to different light radiations. Twenty-four hours later,
cells were processed for immunofluorescence detection of γH2A.x by confocal microscopy. Scale bar: 50 µm. Adapted from [81,84,85] . UVB:
ultraviolet B radiation; VIS: visible light spectrum; wIRA: infrared spectrum
Light radiations
Protection of skin cell types (mostly keratinocytes and skin fibroblasts) against the effects of solar
radiations by this extract of Deschampsia antarctica has been explored in detail. Exposure to this extract
protects human dermal fibroblasts from deleterious effects induced by high-energy UV radiation, including
senescent visual phenotypes, oxidative DNA damage (as assessed by DDR hallmarks: poly-ADP ribose
polymerase cleavage and H2AX induction), proapoptotic stress signaling (p38/JNK activation, caspase-3
cleavage, and increased autophagy flux), and expression of ECM remodeling enzymes (MMP1) .
[81]
Importantly, recent studies support that Edafence® also counteracts the damaging impact exerted by
[84]
radiation within visible and infrared spectra on both human fibroblasts and keratinocytes . Incubation
with this extract reduces the accumulation of oxidative DNA damage-associated H2AX and the activation
of autophagy and caspase signaling associated with visible light/infrared radiation (VL/IR) exposure [Figure 5].
Accordingly, exposure to Edafence® reverted reduced cell proliferation and the altered expression of ECM
constituents (cathepsin K, MMP1, collagen I, and elastin) in a dose-dependent manner.
As aforementioned, an increasingly studied agent challenging skin homeostasis in modern life is high-
energy blue light, a radiation wavelength emitted by digital devices and therefore reaching our body for
[85]
extensive periods of time. Recent studies mimicking artificial blue light exposure on in vitro cell cultures
revealed that these wavelengths reduce cell viability (an effect more pronounced in melanocytes than in
dermal fibroblasts), promote hyperpigmentation and morphological alterations, and induce mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative stress. Of note, addition of Edafence® counteracted these effects and reduced
oxidative stress and ROS accumulation, mitochondrial homeostasis, and stress markers in fibroblasts, as
well as melanization of keratinocytes .
[85]
The molecular mechanisms at play remain to be fully understood, but both the intrinsic antioxidant
activities of this extract bearing species capable of directly quenching oxidizing radicals as well as its ability
[78]
to boost homeostatic programs in the cell, including endogenous antioxidant responses , could underpin
the protective action of Edafence® against different sources of damaging light radiation.