Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Page 6 of 9 Liang et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2019;6:23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2019.33
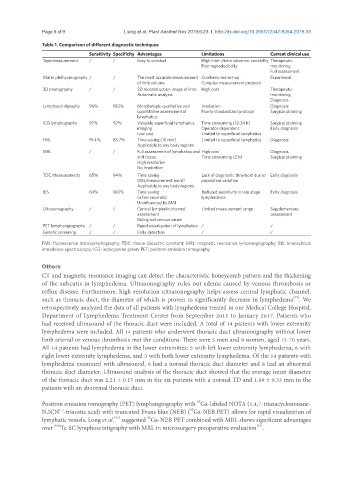
Table 1. Comparison of different diagnostic techniques
Sensitivity Specificity Advantages Limitations Current clinical use
Tape measurement / / Easy to conduct High inter-/intra-observer variability Therapeutic
Poor reproducibility monitoring
Full assessment
Water plethysmography / / The most accurate measurement Cumbersome set-up Experiment
of limb volume Complex measurement protocol
3D photography / / 3D reconstruction image of limb High cost Therapeutic
Automatic analysis monitoring
Diagnosis
Lymphoscintigraphy 96% 100% Morphologic-qualitative and Irradiation Diagnosis
quantitative assessment of Poorly standardized protocol Surgical planning
lymphatics
ICG lymphography 97% 92% Valuable superficial lymphatics Time consuming (12-24 h) Surgical planning
imaging Operator dependent Early diagnosis
Low cost Limited to superficial lymphatics
FML 91.4% 85.7% Time saving (10 min) Limited to superficial lymphatics Diagnosis
Applicable to any body regions
MRL / / Full assessment of lymphatics and High cost Diagnosis
soft tissue Time consuming (2 h) Surgical planning
High resolution
No Irradiation
TDC Measurements 65% 94% Time saving Lack of diagnostic threshold due to Early diagnosis
(10s/measurement point) population variation
Applicable to any body regions
BIS 64% 100% Time saving Reduced sensitivity in late stage Early diagnosis
(a few seconds) lymphedema
Uninfluenced by BMI
Ultrasonography / / Central lymphatic channel Limited measurement range Supplementary
assessment assessment
Ruling out venous cause
PET lymphangiography / / Rapid visualization of lymphatics / /
Genetic screening / / Early detection / /
FML: fluorescence microlymphography; TDC: tissue dielectric constant; MRL: magnetic resonance lymphangiography; BIS: bioelectrical
impedance spectroscopy; ICG: indocyanine green; PET: positron emission tomography
Others
CT and magnetic resonance imaging can detect the characteristic honeycomb pattern and the thickening
of the subcutis in lymphedema. Ultrasonography rules out edema caused by venous thrombosis or
reflux disease. Furthermore, high resolution ultrasonography helps assess central lymphatic channel,
such as thoracic duct, the diameter of which is proven to significantly decrease in lymphedema . We
[32]
retrospectively analyzed the data of all patients with lymphedema treated in our Medical College Hospital,
Department of Lymphedema Treatment Center from September 2015 to January 2017. Patients who
had received ultrasound of the thoracic duct were included. A total of 14 patients with lower extremity
lymphedema were included. All 14 patients who underwent thoracic duct ultrasonography without lower
limb arterial or venous thrombosis met the conditions. There were 5 men and 9 women, aged 15-70 years.
All 14 patients had lymphedema in the lower extremities: 5 with left lower extremity lymphedema, 6 with
right lower extremity lymphedema, and 3 with both lower extremity lymphedema. Of the 14 patients with
lymphedema examined with ultrasound, 6 had a normal thoracic duct diameter and 8 had an abnormal
thoracic duct diameter. Ultrasound analysis of the thoracic duct showed that the average inner diameter
of the thoracic duct was 2.21 ± 0.15 mm in the six patients with a normal TD and 1.99 ± 0.33 mm in the
patients with an abnormal thoracic duct.
68
Positron emission tomography (PET) lymphangiography with Ga-labeled NOTA (1,4,7-triazacyclononane-
68
N,N’,N’ ’-triacetic acid) with truncated Evans blue (NEB) ( Ga-NEB PET) allows for rapid visualization of
[33]
68
lymphatic vessels. Long et al. suggested Ga-NEB PET combined with MRL shows significant advantages
over Tc-SC lymphoscintigraphy with MRL in microsurgery preoperative evaluation .
[33]
99m