Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Van Hove et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:8 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.59 Page 5 of 14
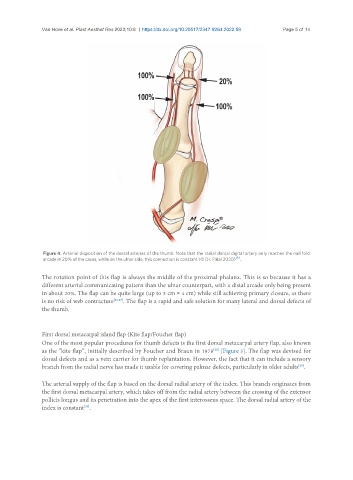
Figure 4. Arterial disposition of the dorsal arteries of the thumb. Note that the radial dorsal digital artery only reaches the nail fold
[6]
arcade in 20% of the cases, while on the ulnar side, this connection is constant (© Dr. Piñal 2020) .
The rotation point of this flap is always the middle of the proximal phalanx. This is so because it has a
different arterial communicating pattern than the ulnar counterpart, with a distal arcade only being present
in about 20%. The flap can be quite large (up to 3 cm × 4 cm) while still achieving primary closure, as there
is no risk of web contracture [26,27] . The flap is a rapid and safe solution for many lateral and dorsal defects of
the thumb.
First dorsal metacarpal island flap (Kite flap/Foucher flap)
One of the most popular procedures for thumb defects is the first dorsal metacarpal artery flap, also known
as the “kite flap”, initially described by Foucher and Braun in 1978 [Figure 5]. The flap was devised for
[28]
dorsal defects and as a vein carrier for thumb replantation. However, the fact that it can include a sensory
[29]
branch from the radial nerve has made it usable for covering palmar defects, particularly in older adults .
The arterial supply of the flap is based on the dorsal radial artery of the index. This branch originates from
the first dorsal metacarpal artery, which takes off from the radial artery between the crossing of the extensor
pollicis longus and its penetration into the apex of the first interosseus space. The dorsal radial artery of the
index is constant .
[28]