Page 27 - Read Online
P. 27
Page 4 of 14 Van Hove et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:8 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.59
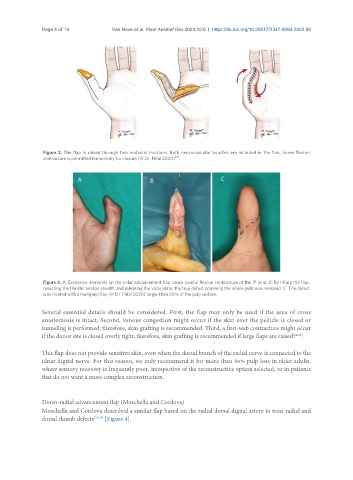
Figure 2. The flap is raised through two midaxial incisions. Both neurovascular bundles are included in the flap. Some flexion
[6]
contracture is permitted temporarily for closure (© Dr. Piñal 2020) .
Figure 3. A: Excessive demands on the volar advancement flap cause painful flexion contracture of the IP joint. B: By lifting the flap,
resecting the fibrotic tendon sheath, and releasing the volar plate, the true defect spanning the whole pulp was revealed. C: The defect
was treated with a hemipulp flap (© Dr. Piñal 2020) larger than 50% of the pulp surface.
Several essential details should be considered. First, the flap may only be used if the area of cross
anastomosis is intact. Second, venous congestion might occur if the skin over the pedicle is closed or
tunneling is performed; therefore, skin grafting is recommended. Third, a first-web contracture might occur
if the donor site is closed overly tight; therefore, skin grafting is recommended if large flaps are raised [24,25] .
This flap does not provide sensitive skin, even when the dorsal branch of the radial nerve is connected to the
ulnar digital nerve. For this reason, we only recommend it for more than 50% pulp loss in older adults,
where sensory recovery is frequently poor, irrespective of the reconstructive option selected, or in patients
that do not want a more complex reconstruction.
Dorso-radial advancement flap (Moschella and Cordova)
Moschella and Cordova described a similar flap based on the radial dorsal digital artery to treat radial and
dorsal thumb defects [21,26] [Figure 4].