Page 260 - Read Online
P. 260
Page 12 of 19 Mondal et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:34 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.13
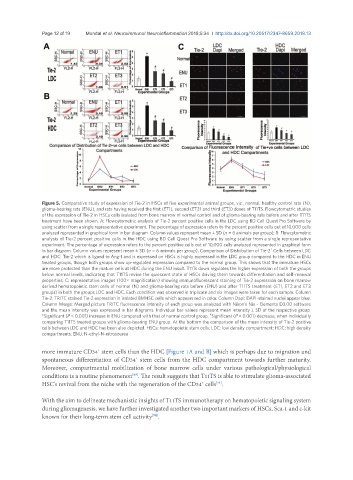
Figure 5. Comparative study of expression of Tie-2 in HSCs of five experimental animal groups, viz., normal, healthy control rats (N),
glioma-bearing rats (ENU), and rats having received the first (ET1), second (ET2) and third (ET3) doses of T11TS. Flowcytometric studies
of the expression of Tie-2 in HSCs cells isolated from bone marrow of normal control and of glioma-bearing rats before and after T11TS
treatment have been shown. A: Flowcytometric analysis of Tie-2 percent positive cells in the LDC using BD Cell Quest Pro Software by
using scatter from a single representative experiment. The percentage of expression refers to the percent positive cells out of 10,000 cells
analyzed represented in graphical form in bar diagram. Column values represent mean ± SD (n = 6 animals per group); B: Flowcytometric
analysis of Tie-2 percent positive cells in the HDC using BD Cell Quest Pro Software by using scatter from a single representative
experiment. The percentage of expression refers to the percent positive cells out of 10,000 cells analyzed represented in graphical form
+
in bar diagram. Column values represent mean ± SD (n = 6 animals per group). Comparison of Distribution of Tie-2 Cells between LDC
and HDC: Tie-2 which is ligand to Ang-1 and is expressed on HSCs is highly expressed in the LDC group compared to the HDC in ENU
treated groups, though both groups show up-regulated expression compared to the normal group. This shows that the immature HSCs
are more protected than the mature cells at HDC during the ENU insult. T11Ts down regulates the higher expression of both the groups
below normal levels, indicating that T11TS revive the quiescent state of HSCs driving them towards differentiation and self-renewal
properties; C: representative images (100× magnification) showing immunofluorescent staining of Tie-2 expression on bone marrow
derived hematopoietic stem cells of normal (N) and glioma-bearing rats before (ENU) and after T11TS treatment (ET1, ET2 and ET3
groups) in both the groups LDC and HDC. Each condition was observed in triplicate and six images were taken for each sample. Column
Tie-2: TRITC stained Tie-2 expression in isolated BMHSC cells which appears red in color. Column Dapi: DAPI-stained nuclei appear blue.
Column Merge: Merged picture TRITC fluorescence intensity of each group was analyzed with Nikon’s Nis - Elements D3.00 software
and the mean intensity was expressed in bar diagrams. Individual bar values represent mean intensity ± SD of the respective group.
#
*Significant (P < 0.001) increase in ENU compared with that of normal control group. Significant (P < 0.001) decrease, when individually
comparing T11TS treated groups with glioma-bearing ENU group. At the bottom the comparison of the mean intensity of Tie-2 positive
cells between LDC and HDC has been also depicted. HSCs: hematopoietic stem cells; LDC: low density compartment; HDC: high density
compartments; ENU: N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea
more immature CD34 stem cells than the HDC [Figure 1A and B] which is perhaps due to migration and
+
spontaneous differentiation of CD34 stem cells from the HDC compartment towards further maturity.
+
Moreover, compartmental mobilization of bone marrow cells under various pathological/physiological
conditions is a routine phenomenon . The result suggests that T11TS is able to stimulate glioma-associated
[69]
HSC’s revival from the niche with the regeneration of the CD34 cells .
+
[41]
With the aim to delineate mechanistic insights of T11TS immunotherapy on hematopoietic signaling system
during gliomagenesis, we have further investigated another two important markers of HSCs, Sca-1 and c-kit
known for their long-term stem cell activity .
[70]