Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Sharma et al. Zinc supplementation prevents against LPS induced neurotoxicity in rats
Table 2: Effect of prenatal zinc supplementation on NO levels, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense system
in mid brain of prenatally LPS treated male and female pups
Catalase (nmoles of
NO (nmoles/mg LPO (nmoles of GSH (µmoles/
Group SOD (I.U) H 2 O 2 hydrolysed/mg
protein) MDA/mg protein) mg protein)
protein/min
Male
Control 0.389 + 0.051 40.11 + 7.64 31.91 + 0.60 0.349 + 0.054 0.700 + 0.120
LPS 0.430 + 0.020 50.03 + 5.54 12.26 + 1.09 * 0.269 + 0.041 0.540 + 0.062
0.314 + 0.038 # 45.41 + 7.60 # 19.69 + 1.68 # 0.290 + 0.035 0.610 + 0.082
LPS + ZnSO 4
0.357 + 0.054 # 36.50 + 9.76 31.25 + 1.34 # 0.340 + 0.033 0.800 + 0.091 #
ZnSO 4
Female
Control 0.299 + 0.028 39.95 + 7.57 29.77 + 1.04 0.607 + 0.013 1.000 + 0.170
LPS 0.438 + 0.022 * 55.13 + 4.79 * 12.01 + 0.70 * 0.407 + 0.050 * 0.670 + 0.083 *
0.321 + 0.066 # 41.14 + 6.50 # 20.84 + 0.68 # 0.470 + 0.050 0.750 + 0.110
LPS + ZnSO 4
0.299 + 0.038 # 27.36 + 4.29 # 29.37 + 0.90 # 0.716 + 0.110 *# 1.160 + 0.180 #
ZnSO 4
#
Values are expressed as mean + SD; n = 5/group. *P < 0.05 vs. control group, P < 0.05 vs. prenatally LPS treated group. LPS:
lipopolysaccharide; NO: nitric oxide; LPO: lipid peroxidation; GSH: reduced glutathione; SOD: superoxide dismutase
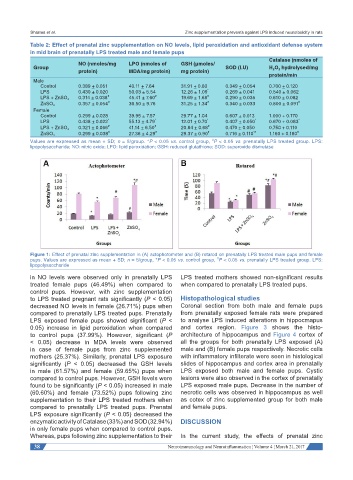
Figure 1: Effect of prenatal zinc supplementation in (A) actophotometer and (B) rotarod on prenatally LPS treated male pups and female
#
pups. Values are expressed as mean + SD; n = 5/group, *P < 0.05 vs. control group, P < 0.05 vs. prenatally LPS treated group. LPS:
lipopolysaccharide
in NO levels were observed only in prenatally LPS LPS treated mothers showed non-significant results
treated female pups (46.49%) when compared to when compared to prenatally LPS treated pups.
control pups. However, with zinc supplementation
to LPS treated pregnant rats significantly (P < 0.05) Histopathological studies
decreased NO levels in female (26.71%) pups when Coronal section from both male and female pups
compared to prenatally LPS treated pups. Prenatally from prenatally exposed female rats were prepared
LPS exposed female pups showed significant (P < to analyse LPS induced alterations in hippocmapus
0.05) increase in lipid peroxidation when compared and cortex region. Figure 3 shows the histo-
to control pups (37.99%). However, significant (P architecture of hippocampus and Figure 4 cortex of
< 0.05) decrease in MDA levels were observed all the groups for both prenatally LPS exposed (A)
in case of female pups from zinc supplemented male and (B) female pups respectively. Necrotic cells
mothers (25.37%). Similarly, prenatal LPS exposure with inflammatory infilterate were seen in histological
significantly (P < 0.05) decreased the GSH levels slides of hippocampus and cortex area in prenatally
in male (61.57%) and female (59.65%) pups when LPS exposed both male and female pups. Cystic
compared to control pups. However, GSH levels were lesions were also observed in the cortex of prenatally
found to be significantly (P < 0.05) increased in male LPS exposed male pups. Decrease in the number of
(60.60%) and female (73.52%) pups following zinc necrotic cells was observed in hippocampus as well
supplementation to their LPS treated mothers when as cotex of zinc supplemented group for both male
compared to prenatally LPS treated pups. Prenatal and female pups.
LPS exposure significantly (P < 0.05) decreased the
enzymatic activity of Catalase (33%) and SOD (32.94%) DISCUSSION
in only female pups when compared to control pups.
Whereas, pups following zinc supplementation to their In the current study, the effects of prenatal zinc
38 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ March 21, 2017