Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
Meenakshi-Sundaram et al. SPECT observations in RPL syndrome
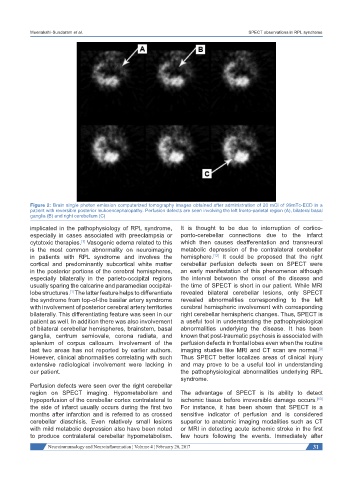
Figure 2: Brain single photon emission computerized tomography images obtained after administration of 20 mCi of 99mTc-ECD in a
patient with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy. Perfusion defects are seen involving the left fronto-parietal region (A), bilateral basal
ganglia (B) and right cerebellum (C)
implicated in the pathophysiology of RPL syndrome, It is thought to be due to interruption of cortico-
especially in cases associated with preeclampsia or ponto-cerebellar connections due to the infarct
[1]
cytotoxic therapies. Vasogenic edema related to this which then causes deafferentation and transneural
is the most common abnormality on neuroimaging metabolic depression of the contralateral cerebellar
[12]
in patients with RPL syndrome and involves the hemisphere. It could be proposed that the right
cortical and predominantly subcortical white matter cerebellar perfusion defects seen on SPECT were
in the posterior portions of the cerebral hemispheres, an early manifestation of this phenomenon although
especially bilaterally in the parieto-occipital regions the interval between the onset of the disease and
usually sparing the calcarine and paramedian occipital- the time of SPECT is short in our patient. While MRI
lobe structures. The latter feature helps to differentiate revealed bilateral cerebellar lesions, only SPECT
[1]
the syndrome from top-of-the basilar artery syndrome revealed abnormalities corresponding to the left
with involvement of posterior cerebral artery territories cerebral hemispheric involvement with corresponding
bilaterally. This differentiating feature was seen in our right cerebellar hemispheric changes. Thus, SPECT is
patient as well. In addition there was also involvement a useful tool in understanding the pathophysiological
of bilateral cerebellar hemispheres, brainstem, basal abnormalities underlying the disease. It has been
ganglia, centrum semiovale, corona radiata, and known that post-traumatic psychosis is associated with
splenium of corpus callosum. Involvement of the perfusion defects in frontal lobes even when the routine
last two areas has not reported by earlier authors. imaging studies like MRI and CT scan are normal.
[9]
However, clinical abnormalities correlating with such Thus SPECT better localizes areas of clinical injury
extensive radiological involvement were lacking in and may prove to be a useful tool in understanding
our patient. the pathophysiological abnormalities underlying RPL
syndrome.
Perfusion defects were seen over the right cerebellar
region on SPECT imaging. Hypometabolism and The advantage of SPECT is its ability to detect
hypoperfusion of the cerebellar cortex contralateral to ischemic tissue before irreversible damage occurs.
[13]
the side of infarct usually occurs during the first two For instance, it has been shown that SPECT is a
months after infarction and is referred to as crossed sensitive indicator of perfusion and is considered
cerebellar diaschisis. Even relatively small lesions superior to anatomic imaging modalities such as CT
with mild metabolic depression also have been noted or MRI in detecting acute ischemic stroke in the first
to produce contralateral cerebellar hypometabolism. few hours following the events. Immediately after
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ February 20, 2017 31