Page 207 - Read Online
P. 207
Zhu et al. Endoglin and cerebral vascular diseases
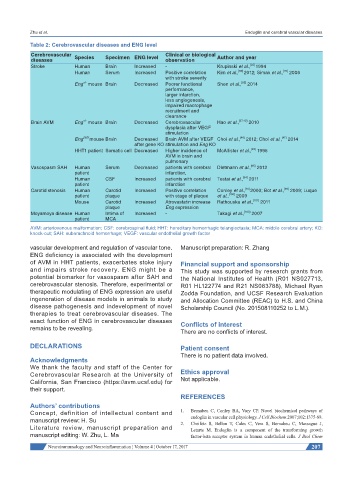
Table 2: Cerebrovascular diseases and ENG level
Cerebrovascular Species Specimen ENG level Clinical or biological Author and year
diseases observation
Stroke Human Brain Increased - Krupinski et al., [22] 1994
Human Serum Increased Positive correlation Kim et al., [69] 2012; Simak et al., [70] 2006
with stroke severity
+/-
[50]
Eng mouse Brain Decreased Poorer functional Shen et al., 2014
performance,
larger infarction,
less angiogenesis,
impaired macrophage
recruitment and
clearance
+/-
Brain AVM Eng mouse Brain Decreased Cerebrovascular Hao et al., [37,40] 2010
dysplasia after VEGF
stimulation
[47]
Eng 2f/2f mouse Brain Decreased Brain AVM after VEGF Choi et al., 2012; Choi et al., 2014
[46]
after gene KO stimulation and Eng KO
[24]
HHT1 patient Somatic cell Decreased Higher incidence of McAllister et al., 1995
AVM in brain and
pulmonary
Vasospasm SAH Human Serum Decreased patients with cerebral Dietmann et al., [95] 2012
patient infarction,
Human CSF Increased patients with cerebral Testai et al., 2011
[94]
patient infarction
[99]
Carotid stenosis Human Carotid Increased Positive correlation Conley et al., [10] 2000; Bot et al., 2009; Luque
patient plaque with stage of plaque et al., [100] 2009
Mouse Carotid Increased Atrovastatin increase Rathouska et al., [101] 2011
plaque Eng expression
Moyamoya disease Human Intima of Increased - Takagi et al., [103] 2007
patient MCA
AVM: arteriovenous malformation; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; HHT: hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia; MCA: middle cerebral artery; KO:
knock-out; SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor
vascular development and regulation of vascular tone. Manuscript preparation: R. Zhang
ENG deficiency is associated with the development
of AVM in HHT patients, exacerbates stoke injury Financial support and sponsorship
and impairs stroke recovery. ENG might be a This study was supported by research grants from
potential biomarker for vasospasm after SAH and the National Institutes of Health (R01 NS027713,
cerebrovascular stenosis. Therefore, experimental or R01 HL122774 and R21 NS083788), Michael Ryan
therapeutic modulating of ENG expression are useful Zodda Foundation, and UCSF Research Evaluation
ingeneration of disease models in animals to study and Allocation Committee (REAC) to H.S. and China
disease pathogenesis and indevelopment of novel Scholarship Council (No. 201508110252 to L.M.).
therapies to treat cerebrovascular diseases. The
exact function of ENG in cerebrovascular diseases Conflicts of interest
remains to be revealing.
There are no conflicts of interest.
DECLARATIONS Patient consent
There is no patient data involved.
Acknowledgments
We thank the faculty and staff of the Center for
Cerebrovascular Research at the University of Ethics approval
California, San Francisco (https://avm.ucsf.edu) for Not applicable.
their support.
REFERENCES
Authors’ contributions
Concept, definition of intellectual content and 1. Bernabeu C, Conley BA, Vary CP. Novel biochemical pathways of
endoglin in vascular cell physiology. J Cell Biochem 2007;102:1375-88.
manuscript review: H. Su 2. Cheifetz S, Bellon T, Cales C, Vera S, Bernabeu C, Massague J,
Literature review, manuscript preparation and Letarte M. Endoglin is a component of the transforming growth
manuscript editing: W. Zhu, L. Ma factor-beta receptor system in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ October 17, 2017 207