Page 156 - Read Online
P. 156
Lu et al. Microbleeds and inflammatory marker levels
MoCA Scores or the using rate of antithrombotic Relations between CMBs and inflammatory
drugs between the CMB group and no CMB group marker levels
(P < 0.05, Table 1). Furthermore, we also observed We observed that serum hs-CRP, IL-6 and MMP-9
similar associations between traditional risk factors levels (median: 6.83, 8.23, 15.98, respectively) in the
and deep or infratentorial CMBs [Table 2]. Similarly, CMB group were higher than in those (median: 3.20,
there were significant differences such as age, or the 5.59, 11.66, respectively) without CMB group [Table 1].
prevalence of alcohol intake, SLI and WML between Similarly, we observed that hs-CRP, IL-6 and MMP-9
the lobar CMB and no CMB group (P < 0.05, Table 2). levels were higher in the deep or infratentorial CMB
Compared with the lobar CMB group, there was higher group (median: 7.01, 9.31, 17.63, respectively) or lobar
prevalence of hypertension and lower alcohol intake CMB group (median: 6.82, 7.98, 15.84, respectively)
in deep or infratentorial CMB group [Table 2]. On than in those without [Table 2]. There was no significant
logistic regression analysis, the association between difference between the deep or infratentorial CMB
traditional risk factors and CMBs are summarized group and lobar CMB group. Connections between
in Table 3. The ORs (per 1SD increase; 95% CI) of CMB and inflammatory markers are summarized in
Table 4. Logistic regression analysis showed that each
age, the prevalence of hypertension, SLI and WML, 1SD-increase in each inflammatory marker level was
MoCA Score and the using rate of antithrombotic significantly associated with the presence of CMB
drugs were 1.666 (1.062-2.632), 2.634 (1.067-4.767), after adjustment for age and sex (Model 1). After
2.345 (1.056-5.226), 1.717 (1.132-2.603), 1.198 adjustment for age, sex, BMI, smoking, alcohol intake,
(1.023-2.268) and 1.234 (1.116-2.584), respectively. hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart
In addition, the association between traditional risk disease, the useful of antithrombotic drugs and the
factors and deep or infratentorial CMBs were also presence of SLI and WML, inflammatory marker level
stronger [Table 3]. However, for strictly lobar CMB, remained to be associated with CMB (Model 2).
the only independent risk factor was age and the
prevalence of alcohol intake [Table 3]. The adjusted ORs of hs-CRP, IL-6 and MMP-9
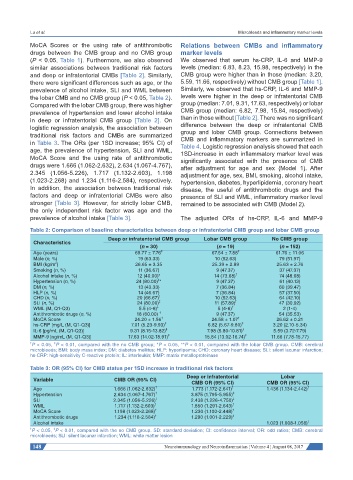
Table 2: Comparison of baseline characteristics between deep or infratentorial CMB group and lobar CMB group
Deep or infratentorial CMB group Lobar CMB group No CMB group
Characteristics
(n = 30) (n = 19) (n = 152)
Age (years) 69.77 ± 7.76 ‡ 67.54 ± 7.88 ‡ 61.76 ± 11.06
Male (n, %) 19 (63.33) 10 (52.63) 79 (51.97)
2
BMI (kg/m ) 26.65 ± 3.35 25.39 ± 2.89 25.63 ± 2.76
Smoking (n, %) 11 (36.67) 9 (47.37) 37 (47.37)
Alcohol intake (n, %) 12 (40.00)* 14 (73.68) † 74 (48.68)
‡
Hypertension (n, %) 24 (80.00) * 9 (47.37) 61 (40.13)
DM (n, %) 13 (43.33) 7 (36.84) 60 (39.47)
HLP (n, %) 14 (46.67) 7 (36.84) 57 (37.50)
CHD (n, %) 20 (66.67) † 10 (52.63) 64 (42.10)
SLI (n, %) 24 (80.00) ‡ 11 (57.89) † 47 (30.92)
WML (M, Q1-Q3) 5.5 (4-6) ‡ 5 (4-6) † 2 (1-4)
Antithrombotic drugs (n, %) 18 (60.00) † 9 (47.37) 54 (35.53)
MoCA Score 24.20 ± 1.56 ‡ 24.58 ± 1.07 † 26.62 ± 0.21
hs-CRP [mg/L (M, Q1-Q3)] 7.01 (5.23-9.93) ‡ 6.82 (5.67-9.80) ‡ 3.20 (2.10-5.34)
IL-6 [pg/mL (M, Q1-Q3)] 9.31 (8.15-13.82) ‡ 7.98 (5.80-10.81) ‡ 5.59 (3.72-7.79)
MMP-9 [ng/mL (M, Q1-Q3)] 17.63 (14.02-18.91) ‡ 15.84 (13.02-16.74) ‡ 11.66 (7.78-15.77)
‡
† P < 0.05, P < 0.01, compared with the no CMB group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with the lobar CMB group. CMB: cerebral
microbleeds; BMI: body mass index; DM: diabetes mellitus; HLP: hyperlipemia; CHD: coronary heart disease; SLI: silent lacunar infarction;
hs-CRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IL: interleukin; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase
Table 3: OR (95% CI) for CMB status per 1SD increase in traditional risk factors
Deep or infratentorial Lobar
Variable CMB OR (95% CI)
CMB OR (95% CI) CMB OR (95% CI)
Age 1.666 (1.062-2.632) † 1.773 (1.172-2.641) † 1.436 (1.134-2.442) †
Hypertension 2.634 (1.067-4.767) † 3.875 (1.795-5.955) ‡
SLI 2.345 (1.056-5.226) † 2.438 (1.226-4.750) ‡
WML 1.717 (1.132-2.603) † 1.850 (1.291-2.643) †
MoCA Score 1.198 (1.023-2.268) † 1.230 (1.100-2.448) †
Antithrombotic drugs 1.234 (1.116-2.584) † 1.290 (1.001-2.229) ‡
Alcohol intake 1.023 (1.008-1.058) †
‡
† P < 0.05, P < 0.01, compared with the no CMB group. SD: standard deviation; CI: confidence interval; OR: odd ratios; CMB: cerebral
microbleeds; SLI: silent lacunar infarction; WML: white matter lesion
148 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ August 08, 2017