Page 155 - Read Online
P. 155
Lu et al. Microbleeds and inflammatory marker levels
microbleeds (basal ganglia, thalamus, brainstem kit; R&D System). The detectable limit for Serum
and cerebellum). Further, we made categories for IL-6 and MMP-9 were 0.01 pg/mL and 0.01 ng/mL,
[11]
“strictly lobar microbleeds” (persons with ≥ 1 new respectively.
microbleeds restricted to a lobar location) and “deep
or infratentorial microbleeds” (persons with ≥ 1 new Statistical analysis
microbleeds in a deep or infratentorial location with or Data was analyzed using SPSS 19.0. Measurement
without lobar microbleeds). [12] Silent lacunar infarction data was described as mean ± standard deviation
was defined as an area of low signal intensity on (SD). Enumeration data was described as number (%).
T1-weighted images with corresponding high signal T-test and one-way analysis of variance was used for
intensity on T2-weighted images, whose diameter comparisons of continuous variables. We used χ test
2
was > 3 mm and < 15 mm (e.g. dilated perivascular for enumeration data. Skewed distribution data was
space). [13] Diagnostic criteria of white matter lesion: described as (Media and Q1-Q3). Kruskal-Wallis test
periventricular white matter lesions (WMLs) were followed by the Mann-Whitney U test were used for
scored according to the following patterns: no lesions comparisons between groups. Multivariate logistic
(0 points); pencil-like or cap-like thin lesions (1 point); regression analyses were used for calculation of odds
smooth haloes at lesion site (2 points); and irregular ratio, in which logarithmically transformed values
periventricular high signals extending to deep WM of inflammatory markers were used. The results are
(3 points). Deep WMLs were scored according to the shown as the odd ratios (OR) with 95% confidence
following patterns: no lesions (0 points); punctate interval (CI). Probability values were 2-tailed, and
separate lesions (1 point); fused lesions (2 points); values of P < 0.05 were considered significant.
and large fused lesions (3 points).The total score
was obtained by adding the periventricular and deep RESULTS
WMLs scales together. [14]
CMB distributional characteristics
Measurement of inflammatory markers Of the patients, 49 (24.38%) had CMBs. The spatial
Blood was drawn with minimally traumatic distribution of the CMB number and location was
venipuncture for measurement of serum inflammatory as follows: deep or infratentorial, 166 in 30 patients
markers. Blood were centrifuged by 3,000 g for 15 min (61.22%); lobar, 88 in 19 patients (38.78%).
at 4 °C, and then aliquots were stored at -70 °C.
Serum hs-CRP was measured by latex turbidimetric Relations between CMBs and traditional risk
immunoassay with a sensitivity of 0.01 mg/L. Serum factors
IL-6 and MMP-9 were measured by enzyme-linked The baseline characteristics of the patients in this study
immunosorbent assay (High Sensitivity Quantikine are shown in Tables 1 and 2. There were significant
kit; R&D System) with a sensitivity of 0.01 pg/mL. differences in the traditional risk factors such as
Serum MMP-9 was also measured by enzyme-linked age, the prevalence of hypertension, coronary heart
immunosorbent assay (High Sensitivity Quantikine disease, silent lacunar infarction (SLI) and WMLs,
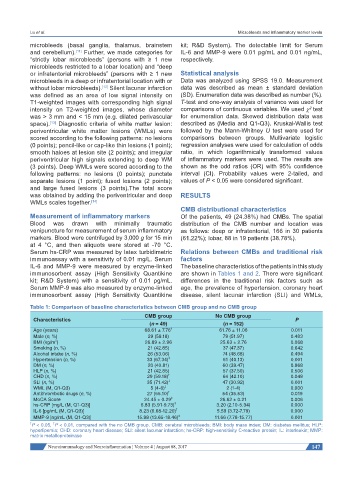
Table 1: Comparison of baseline characteristics between CMB group and no CMB group
CMB group No CMB group
Characteristics P
(n = 49) (n = 152)
Age (years) 68.61 ± 7.76 † 61.76 ± 11.06 0.011
Male (n, %) 29 (59.18) 79 (51.97) 0.483
2
BMI (kg/m ) 26.89 ± 2.96 25.63 ± 2.76 0.068
Smoking (n, %) 21 (42.85) 37 (47.37) 0.642
Alcohol intake (n, %) 26 (53.06) 74 (48.68) 0.494
Hypertension (n, %) 33 (67.34) ‡ 61 (40.13) 0.001
DM (n, %) 20 (40.81) 60 (39.47) 0.868
HLP (n, %) 21 (42.85) 57 (37.50) 0.506
CHD (n, %) 29 (59.18) † 64 (42.10) 0.048
SLI (n, %) 35 (71.42) ‡ 47 (30.92) 0.001
WML (M, Q1-Q3) 5 (4-6) ‡ 2 (1-4) 0.000
Antithrombotic drugs (n, %) 27 (55.10) † 54 (35.53) 0.019
MoCA Score 24.45 ± 0.29 ‡ 26.62 ± 0.21 0.006
hs-CRP [mg/L (M, Q1-Q3)] 6.83 (5.91-9.73) ‡ 3.20 (2.10-5.34) 0.000
IL-6 [pg/mL (M, Q1-Q3)] 8.23 (6.68-12.20) ‡ 5.59 (3.72-7.79) 0.000
MMP-9 [ng/mL (M, Q1-Q3)] 15.98 (13.65-18.46) ‡ 11.66 (7.78-15.77) 0.001
† P < 0.05, P < 0.01, compared with the no CMB group. CMB: cerebral microbleeds; BMI: body mass index; DM: diabetes mellitus; HLP:
‡
hyperlipemia; CHD: coronary heart disease; SLI: silent lacunar infarction; hs-CRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IL: interleukin; MMP:
matrix metalloproteinase
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ August 08, 2017 147