Page 231 - Read Online
P. 231
Menon et al. Pediatric anti-GAD antibody mediated encephalitis
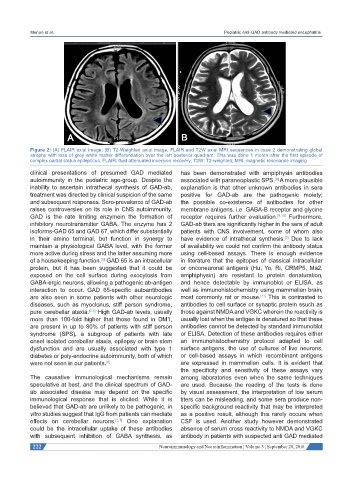
Figure 2: (A) FLAIR axial image; (B) T2-Weighted axial image. FLAIR and T2W axial MRI sequences in case 2 demonstrating global
atrophy with loss of grey white matter differentiation over the left posterior quadrant. This was done 1 month after the first episode of
complex partial status epilepticus. FLAIR: fluid attenuated inversion recovery; T2W: T2-weighted; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging
clinical presentations of presumed GAD mediated has been demonstrated with ampiphysin antibodies
autoimmunity in the pediatric age-group. Despite the associated with paraneoplastic SPS. A more plausible
[8]
inability to ascertain intrathecal synthesis of GAD-ab, explanation is that other unknown antibodies in sera
treatment was directed by clinical suspicion of the same positive for GAD-ab are the pathogenic moiety;
and subsequent responses. Sero-prevalence of GAD-ab the possible co-existence of antibodies for other
raises controversies on its role in CNS autoimmunity. membrane antigens, i.e. GABA-B receptor and glycine
GAD is the rate limiting enzymein the formation of receptor requires further evaluation. [9,10] Furthermore,
inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. The enzyme has 2 GAD-ab titers are significantly higher in the sera of adult
isoforms-GAD 65 and GAD 67, which differ substantially patients with CNS involvement, some of whom also
in their amino terminal, but function in synergy to have evidence of intrathecal synthesis. Due to lack
[2]
maintain a physiological GABA level, with the former of availability we could not confirm the antibody status
more active during stress and the latter assuming more using cell-based assays. There is enough evidence
of a housekeeping function. GAD 65 is an intracellular in literature that the epitopes of classical intracellular
[5]
protein, but it has been suggested that it could be or onconeuronal antigens (Hu, Yo, Ri, CRMP5, Ma2,
exposed on the cell surface during exocytosis from amphiphysin) are resistant to protein denaturation,
GABA-ergic neurons, allowing a pathogenic ab-antigen and hence detectable by immunoblot or ELISA, as
interaction to occur. GAD 65-specific autoantibodies well as immunohistochemistry using mammalian brain,
are also seen in some patients with other neurologic most commonly rat or mouse. This is contrasted to
[11]
diseases, such as myoclonus, stiff person syndrome, antibodies to cell surface or synaptic protein ssuch as
pure cerebellar ataxia. [2,5] High GAD-ab levels, usually those against NMDA and VGKC wherein the reactivity is
more than 100-fold higher that those found in DM1, usually lost when the antigen is denatured so that these
are present in up to 80% of patients with stiff person antibodies cannot be detected by standard immunoblot
syndrome (SPS), a subgroup of patients with late or ELISA. Detection of these antibodies requires either
onset isolated cerebellar ataxia, epilepsy or brain stem an immunohistochemistry protocol adapted to cell
dysfunction and are usually associated with type 1 surface antigens, the use of cultures of live neurons,
diabetes or poly-endocrine autoimmunity, both of which or cell-based assays in which recombinant antigens
were not seen in our patients. [6] are expressed in mammalian cells. It is evident that
the specificity and sensitivity of these assays vary
The causative immunological mechanisms remain among laboratories even when the same techniques
speculative at best, and the clinical spectrum of GAD- are used. Because the reading of the tests is done
ab associated disease may depend on the specific by visual assessment, the interpretation of low serum
immunological response that is elicited. While it is titers can be misleading, and some sera produce non-
believed that GAD-ab are unlikely to be pathogenic, in specific background reactivity that may be interpreted
vitro studies suggest that IgG from patients can mediate as a positive result, although this rarely occurs when
effects on cerebellar neurons. [3,7] One explanation CSF is used. Another study however demonstrated
could be the intracellular uptake of these antibodies absence of serum cross reactivity to NMDA and VGKC
with subsequent inhibition of GABA synthesis, as antibody in patients with suspected anti GAD mediated
222 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 3 ¦ September 28, 2016