Page 134 - Read Online
P. 134
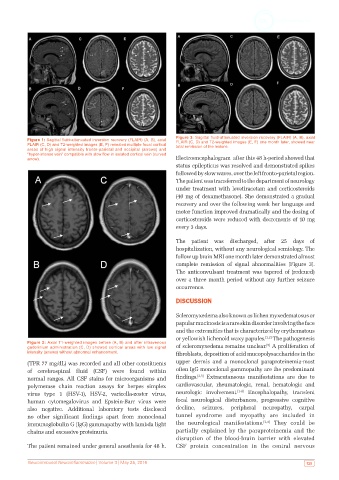
Figure 3: Sagittal fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) (A, B), axial
Figure 1: Sagittal fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) (A, B), axial FLAIR (C, D) and T2-weighted images (E, F) one month later, showed near
FLAIR (C, D) and T2-weighted images (E, F) revealed multiple focal cortical total remission of the lesions.
areas of high signal intensity fronto-parietal and occipital (arrows) and
“hyper-intense vein” compatible with slow flow in isolated cortical vein (curved
arrow). Electroencephalogram after this 48 h-period showed that
status epilepticus was resolved and demonstrated spikes
followed by slow waves, over the left fronto-parietal region.
The patient was transferred to the department of neurology
under treatment with levetiracetam and corticosteroids
(40 mg of dexamethasone). She demonstrated a gradual
recovery and over the following week her language and
motor function improved dramatically and the dosing of
corticosteroids were reduced with decrements of 10 mg
every 3 days.
The patient was discharged, after 25 days of
hospitalization, without any neurological semiology. The
follow up brain MRI one month later demonstrated almost
complete remission of signal abnormalities [Figure 3].
The anticonvulsant treatment was tapered of (redcued)
over a three month period without any further seizure
occurrence.
DISCUSSION
Scleromyxedema also known as lichen myxedematosus or
papular mucinosis is a rare skin disorder involving the face
and the extremities that is characterized by erythematous
or yellowish lichenoid waxy papules. [1,2] The pathogenesis
Figure 2: Axial T1-weighted images before (A, B) and after intravenous [5]
gadolinium administration (C, D) showed cortical areas with low signal of scleromyxedema remains unclear. A proliferation of
intensity (arrows) without abnormal enhancement. fibroblasts, deposition of acid mucopolysaccharides in the
(TPR 77 mg/dL) was recorded and all other constituents upper dermis and a monoclonal paraproteinemia-most
of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were found within often IgG monoclonal gammopathy are the predominant
normal ranges. All CSF stains for microorganisms and findings. [2,5] Extracutaneous manifestations are due to
polymerase chain reaction assays for herpes simplex cardiovascular, rheumatologic, renal, hematologic and
virus type 1 (HSV-1), HSV-2, varicella-zoster virus, neurologic involvement. [1-4] Encephalopathy, transient
human cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus were focal neurological disturbances, progressive cognitive
also negative. Additional laboratory tests disclosed decline, seizures, peripheral neuropathy, carpal
no other significant findings apart from monoclonal tunnel syndrome and myopathy are included in
immunoglobulin G (IgG) gammapathy with lambda light the neurological manifestations. [2,4] They could be
chains and excessive proteinuria. partially explained by the paraproteinemia and the
disruption of the blood-brain barrier with elevated
The patient remained under general anesthesia for 48 h. CSF protein concentration in the central nervous
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | May 25, 2016 125