Page 216 - Read Online
P. 216
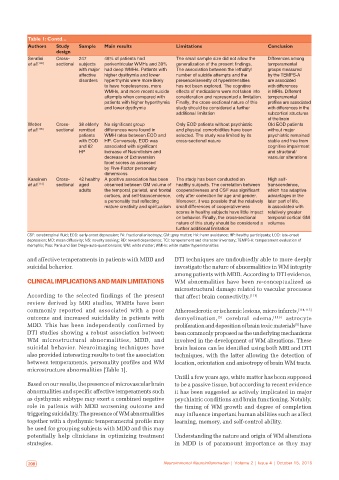
Table 1: Contd...
Authors Study Sample Main results Limitations Conclusion
design
Serafini Cross‑ 247 48% of patients had The small sample size did not allow the Differences among
et al. [106] sectional subjects periventricular WMHs and 39% generalization of the present findings. temperamental
with major had deep WMHs. Patients with The association between the lethality/ groups measured
affective higher dysthymia and lower number of suicide attempts and the by the TEMPS‑A
disorders hyperthymia were more likely presence/severity of hyperintensities are associated
to have hopelessness, more has not been explored. The cognitive with differences
WMHs, and more recent suicide effects of medications were not taken into in MRIs. Different
attempts when compared with consideration and represented a limitation. temperamental
patients with higher hyperthymia Finally, the cross‑sectional nature of this profiles are associated
and lower dysthymia study should be considered a further with differences in the
additional limitation subcortical structures
of the brain
Weber Cross‑ 38 elderly No significant group Only EOD patients without psychiatric Old EOD patients
et al. [105] sectional remitted differences were found in and physical comorbidities have been without major
patients WMH rates between EOD and selected. The study was limited by its psychiatric remained
with EOD HP. Conversely, EOD was cross‑sectional nature stable and free from
and 62 associated with significant cognitive impairment
HP increase of Neuroticism and and structural/
decrease of Extraversion vascular alterations
facet scores as assessed
by Five‑Factor personality
dimensions
Kaasinen Cross‑ 42 healthy A positive association has been The study has been conducted on High self‑
et al. [113] sectional aged observed between GM volume of healthy subjects. The correlation between transcendence,
adults the temporal, parietal, and frontal cooperativeness and CSF was significant which has adaptive
cortices, and self‑transcendence, only after correction for age and gender. advantages in the
a personality trait reflecting Moreover, it was possible that the relatively later part of life,
mature creativity and spiritualism small differences of cooperativeness is associated with
scores in healthy subjects have little impact relatively greater
on behavior. Finally, the cross‑sectional temporal cortical GM
nature of this study should be considered a volumes
further additional limitation
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; EOD: early‑onset depression; FA: fractional anisotropy; GM: grey matter; HA: harm avoidance; HP: healthy participants; LOD: late‑onset
depression; MD: mean diffusivity; NS: novelty seeking; RD: reward dependence; TCI: temperament and character inventory; TEMPS‑A: temperament evaluation of
memphis; Pisa: Paris and San Diego‑auto‑questionnaire; WM: white matter; WMHs: white matter hyperintensities
and affective temperaments in patients with MDD and DTI techniques are undoubtedly able to more deeply
suicidal behavior. investigate the nature of abnormalities in WM integrity
among patients with MDD. According to DTI evidence,
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS AND MAIN LIMITATIONS WM abnormalities have been re‑conceptualized as
microstructural damage related to vascular processes
According to the selected findings of the present that affect brain connectivity. [111]
review derived by MRI studies, WMHs have been
commonly reported and associated with a poor Atherosclerotic or ischemic lesions, micro infarcts, [114,115]
outcome and increased suicidality in patients with demyelination, cerebral edema, [116] astrocyte
[5]
MDD. This has been independently confirmed by proliferation and deposition of brain toxic materials have
[5]
DTI studies showing a robust association between been commonly proposed as the underlying mechanisms
WM microstructural abnormalities, MDD, and involved in the development of WM alterations. These
suicidal behavior. Neuroimaging techniques have brain lesions can be identified using both MRI and DTI
also provided interesting results to test the association techniques, with the latter allowing the detection of
between temperaments, personality profiles and WM location, orientation and anisotropy of brain WM tracts.
microstructure abnormalities [Table 1].
Untill a few years ago, white matter has been supposed
Based on our results, the presence of microvascular brain to be a passive tissue, but according to recent evidence
abnormalities and specific affective temperaments such it has been suggested as actively implicated in major
as dysthymic subtype may exert a combined negative psychiatric conditions and brain functioning. Notably,
role in patients with MDD worsening outcome and the timing of WM growth and degree of completion
triggering suicidality. The presence of WM abnormalities may influence important human abilities such as affect
together with a dysthymic temperamental profile may learning, memory, and self‑control ability.
be used for grouping subjects with MDD and this may
potentially help clinicians in optimizing treatment Understanding the nature and origin of WM alterations
strategies. in MDD is of paramount importance as they may
208 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 4 | October 15, 2015