Page 48 - Read Online
P. 48
edema. Physical examination revealed fever, skin Biopsy of the lymph nodes from the right cervical
hyperpigmentation, hypertrichosis, multiple chain revealed vascular, follicular, and lymphoid
small peripheral lymph nodes, splenomegaly, hyperplasia, thickening of the mantle zone, and the
pitting edema in the lower extremities, tetraplegia, formation of concentric lymphocytes surrounding the
paraesthesia, and hyporeflexia in all four limbs. germinal center, which were hyalinized, atrophic, and
Routine blood examination revealed thrombocytosis surrounded by blood vessels. Vascular proliferation
9
(527 × 10 platelets/L; normal = (101–320) × 10 was found, in addition to sinus histiocytosis in the
9
platelets/L). Blood biochemistry analysis revealed low interfollicular parenchyma [Figure 2]. Meanwhile,
albumin and globulin. Laboratory tests on admission immunohistochemical analysis revealed positive
were positive for hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis staining for CD3, CD4, CD8, CD20, CD21,
B core antibody, and hepatitis B e-antibody, but serum CD138, kappa, lambda, Pax-5, and Ki-67. These
hepatitis B virus (HBV)-DNA was within normal histological findings are consistent with the hyaline
limits. Fibrinogen was 4.72 g/L (normal = 1.8–3.5 g/L). vascular variant of Castleman disease. Patient
Thyroid function test revealed hypothyroidism. improvement was not apparent after treatment
C-reactive protein was 22.60 mg/L, and erythrocyte with dexamethasone for 10 days. The patient was
sedimentation rate was 40 mm/h. Lumbar puncture transferred to the Hematology Department for further
was performed on admission, and cerebrospinal treatment.
fluid testing revealed increased protein and
pressure levels, but the cell count was normal. DISCUSSION
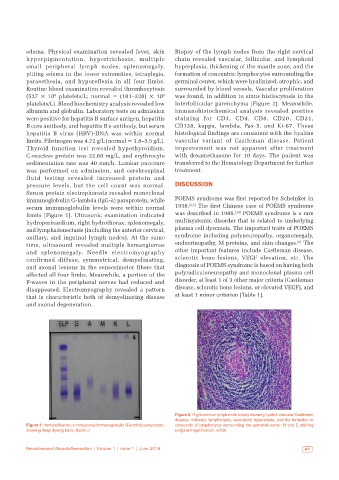
Serum protein electrophoresis revealed monoclonal
immunoglobulin G-lambda (IgG-λ) paraprotein, while POEMS syndrome was first reported by Scheinker in
serum immunoglobulin levels were within normal 1938. [2,5] The first Chinese case of POEMS syndrome
limits [Figure 1]. Ultrasonic examination indicated was described in 1986. [14] POEMS syndrome is a rare
hydropericardium, right hydrothorax, splenomegaly, multisystemic disorder that is related to underlying
and lymphadenectasis (including the anterior cervical, plasma cell dyscrasia. The important traits of POEMS
axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes). At the same syndrome including polyneuropathy, organomegaly,
[6]
time, ultrasound revealed multiple hemangiomas endocrinopathy, M proteins, and skin changes. The
and splenomegaly. Needle electromyography other important features include Castleman disease,
confirmed diffuse, symmetrical, demyelinating, sclerotic bone lesions, VEGF elevation, etc. The
and axonal lesions in the sensorimotor fibers that diagnosis of POEMS syndrome is based on having both
affected all four limbs. Meanwhile, a portion of the polyradiculoneuropathy and monoclonal plasma cell
F-waves in the peripheral nerves had reduced and disorder, at least 1 of 3 other major criteria (Castleman
disappeared. Electromyography revealed a pattern disease, sclerotic bone lesions, or elevated VEGF), and
that is characteristic both of demyelinating disease at least 1 minor criterion [Table 1].
and axonal degeneration.
Figure 2: Right cervical lymph node biopsy showing hyaline vascular Castleman
disease, follicular, lymphocytes, vascularity hyperplasia, and the formation of
Figure 1: Immunofixation, a monoclonal immunoglobulin G-lambda paraprotein, concentric of lymphocytes surrounding the germinal center. H and E staining
showing deep dyeing belts (Band L) (original magnification, ×200)
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 1 | June 2014 41