Page 106 - Read Online
P. 106
frontal lobes were displaced posteriorly, and there
was reactive edema in both frontal lobes. Contrast-
enhanced computed tomography of the neck, chest,
abdomen and pelvis was normal.
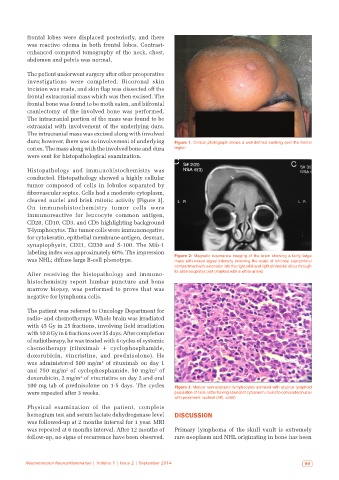
The patient underwent surgery after other preoperative
investigations were completed. Bicoronal skin
incision was made, and skin flap was dissected off the
frontal extracranial mass which was then excised. The
frontal bone was found to be moth eaten, and bifrontal
craniectomy of the involved bone was performed.
The intracranial portion of the mass was found to be
extraaxial with involvement of the underlying dura.
The intracranial mass was excised along with involved
dura; however, there was no involvement of underlying Figure 1: Clinical photograph shows a well-defined swelling over the frontal
cortex. The mass along with the involved bone and dura region
were sent for histopathological examination.
Histopathology and immunohistochemistry was
conducted. Histopathology showed a highly cellular
tumor composed of cells in lobules separated by
fibrovascular septae. Cells had a moderate cytoplasm,
cleaved nuclei and brisk mitotic activity [Figure 3].
On immunohistochemistry tumor cells were
immunoreactive for leucocyte common antigen,
CD20, CD10, CD3, and CD5 highlighting background
T-lymphocytes. The tumor cells were immunonegative
for cytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen, desman,
synaptophysin, CD21, CD30 and S-100. The Mib-1
labeling index was approximately 60%. The impression
was NHL; diffuse large B-cell phenotype. Figure 2: Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain showing a fairly large
mass with mixed signal intensity involving the scalp of bifrontal supraorbital
compartment with extension into the right orbit and right ethmoidal sinus through
After receiving the histopathology and immuno- its anterosuperior part (marked with a white arrow)
histochemistry report lumbar puncture and bone
marrow biopsy, was performed to prove that was
negative for lymphoma cells.
The patient was referred to Oncology Department for
radio- and chemotherapy. Whole brain was irradiated
with 45 Gy in 25 fractions, involving field irradiation
with 10.8 Gy in 6 fractions over 35 days. After completion
of radiotherapy, he was treated with 4 cycles of systemic
chemotherapy (rituximab + cyclophosphamide,
doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone). He
2
was administered 500 mg/m of rituximab on day 1
2
2
and 750 mg/m of cyclophosphamide, 50 mg/m of
2
doxorubicin, 2 mg/m of vincristine on day 2 and oral
100 mg tab of prednisolone on 1-5 days. The cycles Figure 3: Mature nonneoplastic lymphocytes admixed with atypical lymphoid
were repeated after 3 weeks. population of cells, latter having abundant cytoplasm, round to convoluted nuclei
with prominent nucleoli (HE, ×400)
Physical examination of the patient, complete
hemogram test and serum lactate dehydrogenase level DISCUSSION
was followed-up at 2 months interval for 1 year. MRI
was repeated at 6 months interval. After 12 months of Primary lymphoma of the skull vault is extremely
follow-up, no signs of recurrence have been observed. rare neoplasm and NHL originating in bone has been
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 2 | September 2014 99