Page 44 - Read Online
P. 44
Kalloo et al. Metab Target Organ Damage 2023;3:7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mtod.2022.26 Page 5 of 19
significant (win ratio 1.09, 95%CI:
0.97-1.22; P = 0.14)
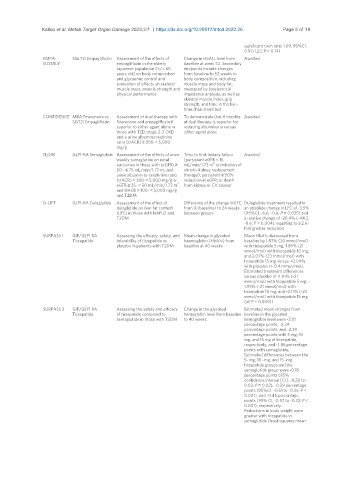
EMPA- SGLT2i Empagliflozin Assessment of the effects of Change in HbA1c level from Awaited
ELDERLY empagliflozin in the elderly baseline at week 52. Secondary
Japanese population (>/= 65 endpoints include changes
years old) on body composition from baseline to 52 weeks in
and glycaemic control and body composition, including
evaluation of effects on skeletal muscle mass and body fat,
muscle mass, muscle strength and measured by bioelectrical
physical performance impedance analysis, as well as
skeletal muscle index, grip
strength, and time in the five-
time chair stand test
CONFIDENCE MRA Finerenone vs Assessment of dual therapy with To demonstrate that 6 months Awaited
SGT2i Empagliflozin finerenone and empagliflozin if of dual therapy is superior for
superior to either agent alone in reducing albuminuria versus
those with T2D, stage 2-3 CKD either agent alone
and a urine albumin:creatinine
ratio (UACR) ≥ 300-< 5,000
mg/g
FLOW GLP1-RA Semaglutide Assessment of the effects of once- Time to first: kidney failure Awaited
weekly semaglutide on renal (persistent eGFR < 15
2
outcomes in those with (eGFR) ≥ mL/min/1.73 m or initiation of
50 - ≤ 75 mL/min/1.73 m and chronic kidney replacement
2
urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio therapy); persistent ≥ 50%
(UACR) > 300-< 5,000 mg/g or reduction in eGFR; or death
2
eGFR ≥ 25- < 50 mL/min/1.73 m from kidney or CV causes
and UACR > 100- < 5,000 mg/g
and T2DM
D-LIFT GLP1-RA Dulaglutide Assessment of the effect of Difference of the change in LFC Dulaglutide treatment resulted in
dulaglutide on liver fat content from 0 (baseline) to 24 weeks an absolute change in LFC of -3.5%
(LFC) in those with NAFLD and between groups (95%CI: -6.6, -0.4; P = 0.025) and
T2DM a relative change of -26.4% (-44.2,
-8.6; P = 0.004), equating to a 2.6-
fold greater reduction
SURPASS 1 GIP/GLP1 RA Assessing the efficacy, safety, and Mean change in glycated Mean HbA1c decreased from
Tirzepatide tolerability of tirzepatide vs haemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline by 1.87% (20 mmol/mol)
placebo in patients with T2DM baseline at 40 weeks with tirzepatide 5 mg, 1.89% (21
mmol/mol) with tirzepatide 10 mg,
and 2.07% (23 mmol/mol) with
tirzepatide 15 mg versus +0.04%
with placebo (+ 0.4 mmol/mol),
Estimated treatment differences
versus placebo of -1.91% (-21
mmol/mol) with tirzepatide 5 mg, -
1.93% (-21 mmol/mol) with
tirzepatide 10 mg, and -2.11% (-23
mmol/mol) with tirzepatide 15 mg
(all P < 0.0001)
SURPASS 2 GIP/GLP1 RA Assessing the safety and efficacy Change in the glycated Estimated mean changes from
Tirzepatide of tirzepatide compared to hemoglobin level from baseline baseline in the glycated
semaglutide in those with T2DM to 40 weeks hemoglobin level were -2.01
percentage points, -2.24
percentage points, and -2.30
percentage points with 5 mg, 10
mg, and 15 mg of tirzepatide,
respectively, and -1.86 percentage
points with semaglutide;
Estimated differences between the
5- mg, 10 -mg, and 15 -mg
tirzepatide groups and the
semaglutide group were -0.15
percentage points (95%
confidence interval [CI], -0.28 to -
0.03; P = 0.02), -0.39 percentage
points (95%CI: -0.51 to -0.26; P <
0.001), and -0.45 percentage
points (95% CI, -0.57 to -0.32; P <
0.001), respectively.
Reductions in body weight were
greater with tirzepatide vs
semaglutide (least-squares mean