Page 174 - Read Online
P. 174
Avery et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.05 Page 11 of 18
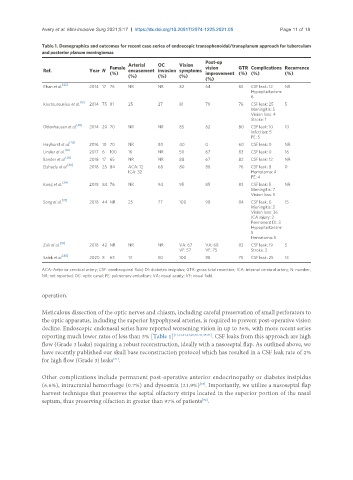
Table 1. Demographics and outcomes for recent case series of endoscopic transsphenoidal/transplanum approach for tuberculum
and posterior planum meningiomas
Post-op
Arterial OC Vision
Female vision GTR Complications Recurrence
Ref. Year N (%) encasement invasion symptoms improvement (%) (%) (%)
(%) (%) (%)
(%)
[42]
Khan et al. 2014 17 76 NR NR 82 64 65 CSF leak: 12 NR
Hypopituitarism:
6
Koutourousiou et al. [13] 2014 75 81 25 27 81 79 76 CSF leak: 25 5
Meningitis: 5
Vision loss: 4
Stroke: 1
[36]
Ottenhausen et al. 2014 20 70 NR NR 85 82 80 CSF leak: 10 10
Infection: 5
PE: 5
Hayhurst et al. [43] 2016 10 70 NR 80 40 0 60 CSF leak: 0 NR
[41]
Linsler et al. 2017 6 100 16 NR 50 67 83 CSF leak: 0 16
Bander et al. [26] 2018 17 65 NR NR 88 67 82 CSF leak: 12 NR
[38]
Elshazly et al. 2018 25 84 ACA: 12 68 80 88 76 CSF leak: 8 0
ICA: 32 Hematoma: 4
PE: 4
Kong et al. [24] 2018 84 76 NR 94 95 85 83 CSF leak: 5 NR
Meningitis: 7
Vision loss: 5
[37]
Song et al. 2018 44 NR 25 77 100 98 84 CSF leak: 0 15
Meningitis: 3
Vision loss: 36
ICA injury: 3
Permanent DI: 3
Hypopituitarism:
5
Hematoma: 5
Zoli et al. [39] 2018 42 NR NR NR VA: 67 VA: 68 83 CSF leak: 19 5
VF: 57 VF: 75 Stroke: 2
[40]
Salek et al. 2020 8 63 13 50 100 88 75 CSF leak: 25 13
ACA: Anterior cerebral artery; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; DI: diabetes insipidus; GTR: gross total resection; ICA: internal cerebral artery; N: number;
NR: not reported; OC: optic canal; PE: pulmonary embolism; VA: visual acuity; VF: visual field.
operation.
Meticulous dissection of the optic nerves and chiasm, including careful preservation of small perforators to
the optic apparatus, including the superior hypophyseal arteries, is required to prevent post-operative vision
decline. Endoscopic endonasal series have reported worsening vision in up to 36%, with more recent series
reporting much lower rates of less than 5% [Table 1] [11,13,23,24,26,36-43,45-51] . CSF leaks from this approach are high
flow (Grade 3 leaks) requiring a robust reconstruction, ideally with a nasoseptal flap. As outlined above, we
have recently published our skull base reconstruction protocol which has resulted in a CSF leak rate of 2%
for high flow (Grade 3) leaks .
[31]
Other complications include permanent post-operative anterior endocrinopathy or diabetes insipidus
(6.6%), intracranial hemorrhage (0.7%) and dysosmia (21.9%) . Importantly, we utilize a nasoseptal flap
[19]
harvest technique that preserves the septal olfactory strips located in the superior portion of the nasal
[52]
septum, thus preserving olfaction in greater than 97% of patients .