Page 172 - Read Online
P. 172
Avery et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.05 Page 9 of 18
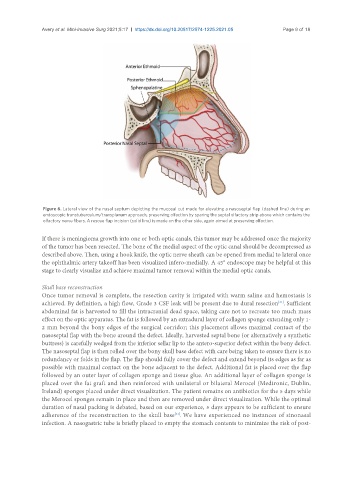
Figure 6. Lateral view of the nasal septum depicting the mucosal cut made for elevating a nasoseptal flap (dashed line) during an
endoscopic transtuberculum/transplanum approach, preserving olfaction by sparing the septal olfactory strip above which contains the
olfactory nerve fibers. A rescue flap incision (solid line) is made on the other side, again aimed at preserving olfaction.
If there is meningioma growth into one or both optic canals, this tumor may be addressed once the majority
of the tumor has been resected. The bone of the medial aspect of the optic canal should be decompressed as
described above. Then, using a hook knife, the optic nerve sheath can be opened from medial to lateral once
the ophthalmic artery takeoff has been visualized infero-medially. A 45° endoscope may be helpful at this
stage to clearly visualize and achieve maximal tumor removal within the medial optic canals.
Skull base reconstruction
Once tumor removal is complete, the resection cavity is irrigated with warm saline and hemostasis is
[31]
achieved. By definition, a high flow, Grade 3 CSF leak will be present due to dural resection . Sufficient
abdominal fat is harvested to fill the intracranial dead space, taking care not to recreate too much mass
effect on the optic apparatus. The fat is followed by an extradural layer of collagen sponge extending only 1-
2 mm beyond the bony edges of the surgical corridor; this placement allows maximal contact of the
nasoseptal flap with the bone around the defect. Ideally, harvested septal bone (or alternatively a synthetic
buttress) is carefully wedged from the inferior sellar lip to the antero-superior defect within the bony defect.
The nasoseptal flap is then rolled over the bony skull base defect with care being taken to ensure there is no
redundancy or folds in the flap. The flap should fully cover the defect and extend beyond its edges as far as
possible with maximal contact on the bone adjacent to the defect. Additional fat is placed over the flap
followed by an outer layer of collagen sponge and tissue glue. An additional layer of collagen sponge is
placed over the fat graft and then reinforced with unilateral or bilateral Merocel (Medtronic, Dublin,
Ireland) sponges placed under direct visualization. The patient remains on antibiotics for the 5 days while
the Merocel sponges remain in place and then are removed under direct visualization. While the optimal
duration of nasal packing is debated, based on our experience, 5 days appears to be sufficient to ensure
adherence of the reconstruction to the skull base . We have experienced no instances of sinonasal
[31]
infection. A nasogastric tube is briefly placed to empty the stomach contents to minimize the risk of post-