Page 832 - Read Online
P. 832
Ancona et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:79 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.80 Page 21 of 23
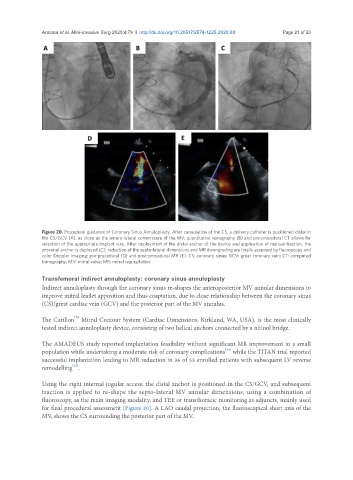
Figure 20. Procedural guidance of Coronary Sinus Annuloplasty. After cannulation of the CS, a delivery catheter is positioned distal in
the CS/GCV (A), as close as the antero-lateral commissure of the MV; quantitative venography (B) and pre-procedural CT allows for
selection of the appropriate implant size. After deployment of the distal anchor of the device and application of manual traction, the
proximal anchor is deployed (C); reduction of the septo-lateral dimensions and MR downgrading are finally assessed by fluoroscopy and
color Doppler imaging: pre-procedural (D) and post-procedural MR (E). CS: coronary sinus; GCV: great coronary vein; CT: computed
tomography; MV: mitral valve; MR: mitral regurgitation
Transfemoral indirect annuloplasty: coronary sinus annuloplasty
Indirect annuloplasty through the coronary sinus re-shapes the anteroposterior MV annular dimensions to
improve mitral leaflet apposition and thus coaptation, due to close relationship between the coronary sinus
(CS)/great cardiac vein (GCV) and the posterior part of the MV annulus.
TM
The Carillon Mitral Contour System (Cardiac Dimensions, Kirkland, WA, USA), is the most clinically
tested indirect annuloplasty device, consisting of two helical anchors connected by a nitinol bridge.
The AMADEUS study reported implantation feasibility without significant MR improvement in a small
[24]
population while undertaking a moderate risk of coronary complications while the TITAN trial reported
successful implantation leading to MR reduction in 36 of 53 enrolled patients with subsequent LV reverse
[25]
remodelling .
Using the right internal jugular access, the distal anchor is positioned in the CS/GCV, and subsequent
traction is applied to re-shape the septo-lateral MV annular dimensions, using a combination of
fluoroscopy, as the main imaging modality, and TEE or transthoracic monitoring as adjuncts, mainly used
for final procedural assessment [Figure 20]. A LAO caudal projection, the fluoroscopical short axis of the
MV, shows the CS surrounding the posterior part of the MV.