Page 782 - Read Online
P. 782
Page 8 of 14 Stolz et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:76 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.69
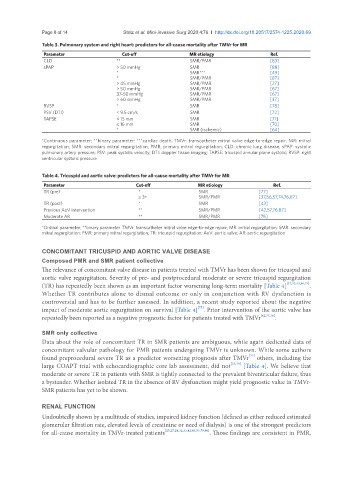
Table 3. Pulmonary system and right heart: predictors for all-cause mortality after TMVr for MR
Parameter Cut-off MR etiology Ref.
CLD ** SMR/PMR [83]
sPAP > 50 mmHg SMR [88]
* SMR*** [49]
* SMR/PMR [87]
> 45 mmHg SMR/PMR [27]
> 50 mmHg SMR/PMR [67]
37-50 mmHg SMR/PMR [67]
> 60 mmHg SMR/PMR [37]
RVSP * SMR [78]
PSV (DTI) < 9.5 cm/s SMR [72]
TAPSE < 15 mm SMR [71]
≤ 16 mm SMR [70]
* SMR (ischemic) [64]
*Continuous parameter; **binary parameter; ***cardiac death. TMVr: transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair; MR: mitral
regurgitation; SMR: secondary mitral regurgitation; PMR: primary mitral regurgitation; CLD: chronic lung disease; sPAP: systolic
pulmonary artery pressure; PSV: peak systolic velocity; DTI: doppler tissue imaging; TAPSE: tricuspid annular plane systolic; RVSP: right
ventricular systolic pressure
Table 4. Tricuspid and aortic valve: predictors for all-cause mortality after TMVr for MR
Parameter Cut-off MR etiology Ref.
TR (pre) * SMR [77]
≥ 3+ SMR/PMR [37,56,57,74,76,87]
TR (post) * SMR [43]
Previous AoV intervention ** SMR/PMR [42,57,76,87]
Moderate AR ** SMR/PMR [75]
*Ordinal parameter; **binary parameter. TMVr: transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair; MR: mitral regurgitation; SMR: secondary
mitral regurgitation; PMR: primary mitral regurgitation; TR: tricuspid regurgitation; AoV: aortic valve; AR: aortic regurgitation
CONCOMITANT TRICUSPID AND AORTIC VALVE DISEASE
Composed PMR and SMR patient collective
The relevance of concomitant valve disease in patients treated with TMVr has been shown for tricuspid and
aortic valve regurgitation. Severity of pre- and postprocedural moderate or severe tricuspid regurgitation
(TR) has repeatedly been shown as an important factor worsening long-term mortality [Table 4] [37,42,43,56,74] .
Whether TR contributes alone to dismal outcome or only in conjunction with RV dysfunction is
controversial and has to be further assessed. In addition, a recent study reported about the negative
[75]
impact of moderate aortic regurgitation on survival [Table 4] . Prior intervention of the aortic valve has
repeatedly been reported as a negative prognostic factor for patients treated with TMVr [42,57,76] .
SMR only collective
Data about the role of concomitant TR in SMR patients are ambiguous, while again dedicated data of
concomitant valvular pathology for PMR patients undergoing TMVr is unknown. While some authors
[77]
found preprocedural severe TR as a predictor worsening prognosis after TMVr others, including the
large COAPT trial with echocardiographic core lab assessment, did not [25,78] [Table 4]. We believe that
moderate or severe TR in patients with SMR is tightly connected to the prevalent biventricular failure, thus
a bystander. Whether isolated TR in the absence of RV dysfunction might yield prognostic value in TMVr-
SMR patients has yet to be shown.
RENAL FUNCTION
Undoubtedly shown by a multitude of studies, impaired kidney function (defined as either reduced estimated
glomerular filtration rate, elevated levels of creatinine or need of dialysis) is one of the strongest predictors
for all-cause mortality in TMVr-treated patients [25,27,28,32,33,42,43,53,79,80] . Those findings are consistent in PMR,