Page 784 - Read Online
P. 784
Page 10 of 14 Stolz et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:76 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.69
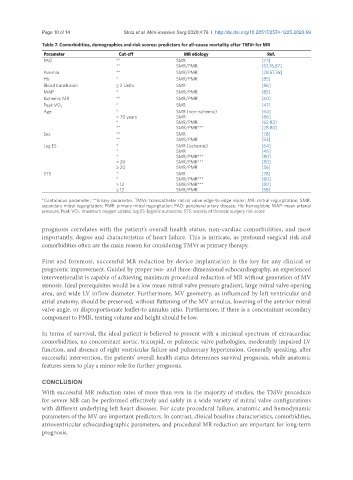
Table 7. Comorbidities, demographics and risk scores: predictors for all-cause mortality after TMVr for MR
Parameter Cut-off MR etiology Ref.
PAD ** SMR [77]
** SMR/PMR [57,76,87]
Anemia ** SMR/PMR [28,57,76]
Hb * SMR/PMR [85]
Blood transfusion ≥ 2 Units SMR [86]
MAP * SMR/PMR [85]
Ischemic MR ** SMR/PMR [60]
* SMR [47]
Peak VO 2
Age * SMR (non-ischemic) [64]
> 70 years SMR [86]
* SMR/PMR [62,83]
** SMR/PMR*** [28,80]
Sex ** SMR [78]
** SMR/PMR [53]
Log ES * SMR (ischemic) [64]
* SMR [45]
* SMR/PMR*** [80]
> 20 SMR/PMR*** [80]
≥ 20 SMR/PMR [36]
STS * SMR [78]
* SMR/PMR*** [80]
≥ 12 SMR/PMR*** [80]
≥ 12 SMR/PMR [58]
*Continuous parameter; **binary parameter. TMVr: transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair; MR: mitral regurgitation; SMR:
secondary mitral regurgitation; PMR: primary mitral regurgitation; PAD: peripheral artery disease; Hb: hemoglobin; MAP: mean arterial
pressure; Peak VO 2 : maximum oxygen uptake; log ES: logistic euroscore; STS: society of thoracic surgery risk score
prognosis correlates with the patient’s overall health status, non-cardiac comorbidities, and most
importantly, degree and characteristics of heart failure. This is intricate, as profound surgical risk and
comorbidities often are the main reason for considering TMVr as primary therapy.
First and foremost, successful MR reduction by device implantation is the key for any clinical or
prognostic improvement. Guided by proper two- and three-dimensional echocardiography, an experienced
interventionalist is capable of achieving maximum procedural reduction of MR without generation of MV
stenosis. Ideal prerequisites would be a low mean mitral valve pressure gradient, large mitral valve opening
area, and wide LV inflow diameter. Furthermore, MV geometry, as influenced by left ventricular and
atrial anatomy, should be preserved, without flattening of the MV annulus, lowering of the anterior mitral
valve angle, or disproportionate leaflet-to annulus ratio. Furthermore, if there is a concomitant secondary
component to PMR, tenting volume and height should be low.
In terms of survival, the ideal patient is believed to present with a minimal spectrum of extracardiac
comorbidities, no concomitant aortic, tricuspid, or pulmonic valve pathologies, moderately impaired LV
function, and absence of right ventricular failure and pulmonary hypertension. Generally speaking, after
successful intervention, the patients’ overall health status determines survival prognosis, while anatomic
features seem to play a minor role for further prognosis.
CONCLUSION
With successful MR reduction rates of more than 95% in the majority of studies, the TMVr procedure
for severe MR can be performed effectively and safely in a wide variety of mitral valve configurations
with different underlying left heart diseases. For acute procedural failure, anatomic and hemodynamic
parameters of the MV are important predictors. In contrast, clinical baseline characteristics, comorbidities,
atrioventricular echocardiographic parameters, and procedural MR reduction are important for long-term
prognosis.