Page 779 - Read Online
P. 779
Stolz et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:76 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.69 Page 5 of 14
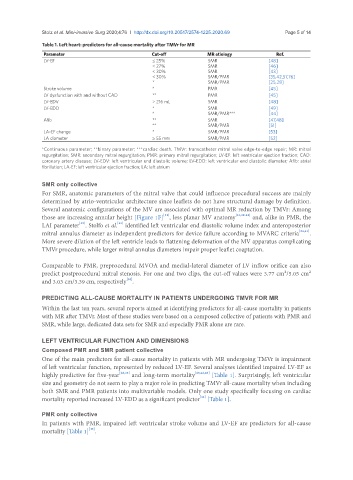
Table 1. Left heart: predictors for all-cause mortality after TMVr for MR
Parameter Cut-off MR etiology Ref.
LV-EF ≤ 25% SMR [48]
< 27% SMR [46]
< 30% SMR [43]
< 30% SMR/PMR [35,42,57,76]
* SMR/PMR [25,28]
Stroke volume * PMR [45]
LV dysfunction with and without CAD ** PMR [45]
LV-EDV > 216 mL SMR [48]
LV-EDD * SMR [49]
* SMR/PMR*** [44]
Afib ** SMR [47,48]
** SMR/PMR [51]
LA-EF change * SMR/PMR [53]
LA diameter ≥ 55 mm SMR/PMR [52]
*Continuous parameter; **binary parameter; ***cardiac death. TMVr: transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair; MR: mitral
regurgitation; SMR: secondary mitral regurgitation; PMR: primary mitral regurgitation; LV-EF: left ventricular ejection fraction; CAD:
coronary artery disease; LV-EDV: left ventricular end diastolic volume; LV-EDD: left ventricular end diastolic diameter; Afib: atrial
fibrillation; LA-EF: left ventricular ejection fraction; LA: left atrium
SMR only collective
For SMR, anatomic parameters of the mitral valve that could influence procedural success are mainly
determined by atrio-ventricular architecture since leaflets do not have structural damage by definition.
Several anatomic configurations of the MV are associated with optimal MR reduction by TMVr: Among
[31]
those are increasing annular height [Figure 1F] , less planar MV anatomy [31,39-41] and, alike in PMR, the
[41]
[32]
LAI parameter . Stolfo et al. identified left ventricular end diastolic volume index and anteroposterior
mitral annulus diameter as independent predictors for device failure according to MVARC criteria [24,41] .
More severe dilation of the left ventricle leads to flattening deformation of the MV apparatus complicating
TMVr procedure, while larger mitral annulus diameters impair proper leaflet coaptation.
Comparable to PMR, preprocedural MVOA and medial-lateral diameter of LV inflow orifice can also
predict postprocedural mitral stenosis. For one and two clips, the cut-off values were 3.77 cm²/5.05 cm²
and 3.03 cm/3.39 cm, respectively .
[38]
PREDICTING ALL-CAUSE MORTALITY IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING TMVR FOR MR
Within the last ten years, several reports aimed at identifying predictors for all-cause mortality in patients
with MR after TMVr. Most of these studies were based on a composed collective of patients with PMR and
SMR, while large, dedicated data sets for SMR and especially PMR alone are rare.
LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION AND DIMENSIONS
Composed PMR and SMR patient collective
One of the main predictors for all-cause mortality in patients with MR undergoing TMVr is impairment
of left ventricular function, represented by reduced LV-EF. Several analyses identified impaired LV-EF as
highly predictive for five-year [28,35] and long-term mortality [25,42,43] [Table 1]. Surprisingly, left ventricular
size and geometry do not seem to play a major role in predicting TMVr all-cause mortality when including
both SMR and PMR patients into multivariable models. Only one study specifically focusing on cardiac
[44]
mortality reported increased LV-EDD as a significant predictor [Table 1].
PMR only collective
In patients with PMR, impaired left ventricular stroke volume and LV-EF are predictors for all-cause
[45]
mortality [Table 1] .