Page 161 - Read Online
P. 161
Bianchi et al. Modified fundoplication after Heller miotomy
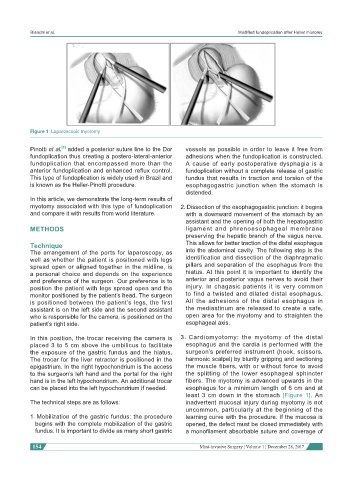
Figure 1: Laparoscopic myotomy
[3]
Pinotti et al. added a posterior suture line to the Dor vessels as possible in order to leave it free from
fundoplication thus creating a postero-lateral-anterior adhesions when the fundoplication is constructed.
fundoplication that encompassed more than the A cause of early postoperative dysphagia is a
anterior fundoplication and enhanced reflux control. fundoplication without a complete release of gastric
This type of fundoplication is widely used in Brazil and fundus that results in traction and torsion of the
is known as the Heller-Pinotti procedure. esophagogastric junction when the stomach is
distended.
In this article, we demonstrate the long-term results of
myotomy associated with this type of fundoplication 2. Dissection of the esophagogastric junction: it begins
and compare it with results from world literature. with a downward movement of the stomach by an
assistant and the opening of both the hepatogastric
METHODS ligament and phrenoesophageal membrane
preserving the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve.
Technique This allows for better traction of the distal esophagus
The arrangement of the ports for laparoscopy, as into the abdominal cavity. The following step is the
well as whether the patient is positioned with legs identification and dissection of the diaphragmatic
spread open or aligned together in the midline, is pillars and separation of the esophagus from the
a personal choice and depends on the experience hiatus. At this point it is important to identify the
and preference of the surgeon. Our preference is to anterior and posterior vagus nerves to avoid their
position the patient with legs spread open and the injury. In chagasic patients it is very common
monitor positioned by the patient’s head. The surgeon to find a twisted and dilated distal esophagus.
is positioned between the patient’s legs, the first All the adhesions of the distal esophagus in
assistant is on the left side and the second assistant the mediastinum are released to create a safe,
who is responsible for the camera, is positioned on the open area for the myotomy and to straighten the
patient’s right side. esophageal axis.
In this position, the trocar receiving the camera is 3. Cardiomyotomy: the myotomy of the distal
placed 3 to 5 cm above the umbilicus to facilitate esophagus and the cardia is performed with the
the exposure of the gastric fundus and the hiatus. surgeon’s preferred instrument (hook, scissors,
The trocar for the liver retractor is positioned in the harmonic scalpel) by bluntly gripping and sectioning
epigastrium. In the right hypochondrium is the access the muscle fibers, with or without force to avoid
to the surgeon’s left hand and the portal for the right the splitting of the lower esophageal sphincter
hand is in the left hypochondrium. An additional trocar fibers. The myotomy is advanced upwards in the
can be placed into the left hypochondrium if needed. esophagus for a minimum length of 6 cm and at
least 3 cm down in the stomach [Figure 1]. An
The technical steps are as follows: inadvertent mucosal injury during myotomy is not
uncommon, particularly at the beginning of the
1. Mobilization of the gastric fundus: the procedure learning curve with the procedure. If the mucosa is
begins with the complete mobilization of the gastric opened, the defect must be closed immediately with
fundus. It is important to divide as many short gastric a monofilament absorbable suture and coverage of
154 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017