Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
Gharagozloo et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:66 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.53 Page 21 of 22
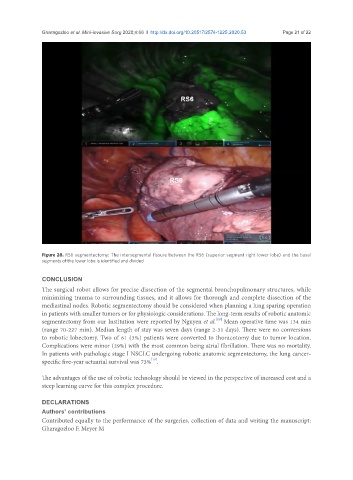
Figure 28. RS6 segmentectomy: The intersegmental fissure between the RS6 (superior segment right lower lobe) and the basal
segments of the lower lobe is identified and divided
CONCLUSION
The surgical robot allows for precise dissection of the segmental bronchopulmonary structures, while
minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues, and it allows for thorough and complete dissection of the
mediastinal nodes. Robotic segmentectomy should be considered when planning a lung sparing operation
in patients with smaller tumors or for physiologic considerations. The long-term results of robotic anatomic
[19]
segmentectomy from our Institution were reported by Nguyen et al. Mean operative time was 134 min
(range 70-227 min). Median length of stay was seven days (range 2-31 days). There were no conversions
to robotic lobectomy. Two of 61 (3%) patients were converted to thoracotomy due to tumor location.
Complications were minor (29%) with the most common being atrial fibrillation. There was no mortality.
In patients with pathologic stage I NSCLC undergoing robotic anatomic segmentectomy, the lung cancer-
[19]
specific five-year actuarial survival was 73% .
The advantages of the use of robotic technology should be viewed in the perspective of increased cost and a
steep learning curve for this complex procedure.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Contributed equally to the performance of the surgeries, collection of data and writing the manuscript:
Gharagozloo F, Meyer M